Onasemnogene abeparvovec in spinal muscular atrophy: an Australian experience of safety and efficacy
- PMID: 35170254
- PMCID: PMC8935277
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51519
Onasemnogene abeparvovec in spinal muscular atrophy: an Australian experience of safety and efficacy
Abstract
Objective: To provide a greater understanding of the tolerability, safety and clinical outcomes of onasemnogene abeparvovec in real-world practice, in a broad population of infants with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
Methods: A prospective cohort study of children with SMA treated with onasemnogene abeparvovec at Sydney Children's Hospital Network, Australia was conducted from August 2019 to November 2021. Safety outcomes included clinical and laboratory evaluations. Efficacy assessments included World Health Organisation (WHO) motor milestones, oral and swallowing abilities, and requirements for respiratory support. The implementation of a model of care for onasemnogene abeparvovec administration in health practice is described.
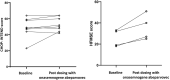
Results: 21 children were treated (age range, 0.65-24 months; body weight range, 2.5-12.5 kg) and 19/21 (90.4%) had previous nusinersen. Transient treatment-related side effects occurred in all children; vomiting (100%), transaminitis (57%) and thrombocytopaenia (33%). Incidence of moderate/severe transaminitis was significantly greater in infants weighing ≥8 kg compared with <8 kg (p < 0.05). Duration of prednisolone following treatment was prolonged (mean 87.5 days, range 57-274 days). 16/21 (76%) children gained at least one WHO motor milestone. Stabilisation or improvement in bulbar or respiratory function was observed in 20/21 (95.2%) patients. Implementation challenges were mitigated by developing standard operating procedures and facilitating exchange of knowledge.
Interpretation: This study provides real-world evidence to inform treatment decisions and guide therapeutic expectations for onasemnogene abeparvovec and combination therapy for SMA in health practice, especially for children weighing ≥8 kg receiving higher vector loads. Proactive clinical and laboratory surveillance is essential to facilitate individualised management of risks.
© 2022 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Farrar and Prof. Ryan have received compensation as a member of scientific advisory boards for Biogen, Roche, and Novartis Gene Therapies. Sandra Holland has received compensation as a member of the scientific advisory board for Novartis Gene Therapies.
All other authors declare no potential conflict of interest. These funding bodies had no role in the design of the study, data collection, data analysis, manuscript design, preparation of the manuscript or decision to publish. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Calucho M, Bernal S, Alías L, et al. Correlation between SMA type and SMN2 copy number revisited: an analysis of 625 unrelated Spanish patients and a compilation of 2834 reported cases. Neuromuscul Disord. 2018;28:208‐215. - PubMed
-
- Mendell JR, Al‐Zaidy S, Shell R, et al. Single‐dose gene‐replacement therapy for spinal muscular atrophy. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1713‐1722. - PubMed
-
- Waldrop MA, Karingada C, Storey MA, et al. Gene therapy for spinal muscular atrophy: safety and early outcomes. Pediatrics. 2020;146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

