Drug-induced Delusional Infestation
- PMID: 35170743
- PMCID: PMC9558340
- DOI: 10.2340/actadv.v102.183
Drug-induced Delusional Infestation
Abstract
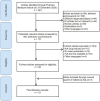
It is considered that certain drugs might induce delusional infestation, yet, to date, no studies have been performed to identify the pharmacodynamics associated with these treatments. The aim of this review is to summarize current available knowledge of drug-induced delusional infestation. A literature search was performed for primary studies on suspected drugs reported to induce delusional infestation. Included articles were evaluated systematically using the Naranjo criteria. In addition, drug mechanisms of action were compared. The final selection included 31 studies, in which a total of 26 classes of drugs were identified. Anti-Parkinson drugs were most frequently associated with delusional infestation, followed by antidepressants, antiepileptics, antibiotics, prescription stimulants, and a few other drug groups. The current available literature suggests that the onset of delusional infestation is initiated by drug-induced alterations in neurotransmitter levels, predominantly dopamine, in the central nervous system.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hughes JE, Barraclough BM, Hamblin LG, White JE. Psychiatric symptoms in dermatology patients. Br J Psychiatry 1983; 143: 51–54. - PubMed
-
- Bewley AP, Lepping P, Freudenmann RW, Taylor R. Delusional parasitosis: time to call it delusional infestation. Br J Dermatol 2010; 163:1–2. Erratum in: Br J Dermatol 2010; 163: 899. - PubMed
-
- Vulink NC. Delusional infestation: state of the art. Acta Derm Venereol 2016; 96: 58–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources