Thermostable ionizable lipid-like nanoparticle (iLAND) for RNAi treatment of hyperlipidemia
- PMID: 35171673
- PMCID: PMC8849333
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abm1418
Thermostable ionizable lipid-like nanoparticle (iLAND) for RNAi treatment of hyperlipidemia
Abstract
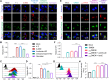
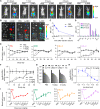
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutic is considered to be a promising modality for the treatment of hyperlipidemia. Establishment of a thermostable clinically applicable delivery system remains a most challenging issue for siRNA drug development. Here, a series of ionizable lipid-like materials were rationally designed; 4 panels of lipid formulations were fabricated and evaluated on the basis of four representative structures. The lead lipid (A1-D1-5) was stable at 40°C, and the optimized formulation (iLAND) showed dose and time dual-dependent gene silencing pattern with median effective dose of 0.18 mg/kg. In addition, potent and durable reduction of serum cholesterol and triglyceride were achieved by administering siRNAs targeting angiopoietin-like 3 or apolipoprotein C3 (APOC3) in high-fat diet-fed mice, db/db mice, and human APOC3 transgenic mice, respectively, accompanied by displaying ideal safety profiles. Therefore, siRNA@iLAND prepared with thermostable A1-D1-5 demonstrates substantial value for siRNA delivery, hyperlipidemia therapy, and prevention of subsequent metabolic diseases.
Figures




References
-
- Gaudet D., Alexander V. J., Baker B. F., Brisson D., Tremblay K., Singleton W., Geary R. S., Hughes S. G., Viney N. J., Graham M. J., Crooke R. M., Witztum J. L., Brunzell J. D., Kastelein J. J., Antisense inhibition of apolipoprotein C-III in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 373, 438–447 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Graham M. J., Lee R. G., Brandt T. A., Tai L. J., Fu W., Peralta R., Yu R., Hurh E., Paz E., McEvoy B. W., Baker B. F., Pham N. C., Digenio A., Hughes S. G., Geary R. S., Witztum J. L., Crooke R. M., Tsimikas S., Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of ANGPTL3 antisense oligonucleotides. N. Engl. J. Med. 377, 222–232 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Macchi C., Sirtori C. R., Corsini A., Santos R. D., Watts G. F., Ruscica M., A new dawn for managing dyslipidemias: The era of rna-based therapies. Pharmacol. Res. 150, 104413 (2019). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

