Personalized chordoma organoids for drug discovery studies
- PMID: 35171675
- PMCID: PMC8849332
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl3674
Personalized chordoma organoids for drug discovery studies
Abstract
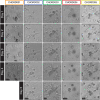
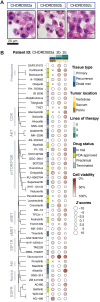
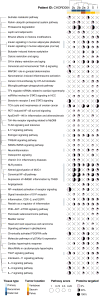
Chordomas are rare tumors of notochordal origin, most commonly arising in the sacrum or skull base. Chordomas are considered insensitive to conventional chemotherapy, and their rarity complicates running timely and adequately powered trials to identify effective treatments. Therefore, there is a need for discovery of novel therapeutic approaches. Patient-derived organoids can accelerate drug discovery and development studies and predict patient responses to therapy. In this proof-of-concept study, we successfully established organoids from seven chordoma tumor samples obtained from five patients presenting with tumors in different sites and stages of disease. The organoids recapitulated features of the original parent tumors and inter- as well as intrapatient heterogeneity. High-throughput screenings performed on the organoids highlighted targeted agents such as PI3K/mTOR, EGFR, and JAK2/STAT3 inhibitors among the most effective molecules. Pathway analysis underscored how the NF-κB and IGF-1R pathways are sensitive to perturbations and potential targets to pursue for combination therapy of chordoma.
Figures


References
-
- Karpathiou G., Dumollard J. M., Dridi M., Dal Col P., Barral F.-G., Boutonnat J., Peoc’h M., Chordomas: A review with emphasis on their pathophysiology, pathology, molecular biology, and genetics. Pathol. Res. Pract. 216, 153089 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Shih A. R., Cote G. M., Chebib I., Choy E., DeLaney T., Deshpande V., Hornicek F. J., Miao R., Schwab J. H., Nielsen G. P., Chen Y.-L., Clinicopathologic characteristics of poorly differentiated chordoma. Mod. Pathol. 31, 1237–1245 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Hasselblatt M., Thomas C., Hovestadt V., Schrimpf D., Johann P., Bens S., Oyen F., Peetz-Dienhart S., Crede Y., Wefers A., Vogel H., Riemenschneider M. J., Antonelli M., Giangaspero F., Bernardo M. C., Giannini C., Din N. U., Perry A., Keyvani K., van Landeghem F., Sumerauer D., Hauser P., Capper D., Korshunov A., Jones D. T. W., Pfister S. M., Schneppenheim R., Siebert R., Frühwald M. C., Kool M., Poorly differentiated chordoma with SMARCB1/INI1 loss: A distinct molecular entity with dismal prognosis. Acta Neuropathol. 132, 149–151 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Choi J. H., Ro J. Y., The 2020 WHO classification of tumors of bone: An updated review. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 28, 119–138 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Hung Y. P., Diaz-Perez J. A., Cote G. M., Wejde J., Schwab J. H., Nardi V., Chebib I. A., Deshpande V., Selig M. K., Bredella M. A., Rosenberg A. E., Nielsen G. P., Dedifferentiated chordoma: Clinicopathologic and molecular characteristics with integrative analysis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 44, 1213–1223 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

