Development of a T cell-based immunodiagnostic system to effectively distinguish SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 vaccination status
- PMID: 35172129
- PMCID: PMC8824221
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.02.003
Development of a T cell-based immunodiagnostic system to effectively distinguish SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 vaccination status
Abstract
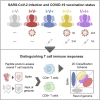
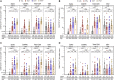
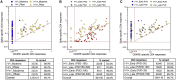
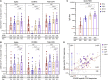
Both SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 vaccines elicit memory T cell responses. Here, we report the development of 2 pools of experimentally defined SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes that, in combination with spike, were used to discriminate 4 groups of subjects with different SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 vaccine status. The overall T cell-based classification accuracy was 89.2% and 88.5% in the experimental and validation cohorts. This scheme was applicable to different mRNA vaccines and different lengths of time post infection/post vaccination and yielded increased accuracy when compared to serological readouts. T cell responses from breakthrough infections were also studied and effectively segregated from vaccine responses, with a combined performance of 86.6% across all 239 subjects from the 5 groups. We anticipate that a T cell-based immunodiagnostic scheme to classify subjects based on their vaccination and natural infection history will be an important tool for longitudinal monitoring of vaccinations and for establishing SARS-CoV-2 correlates of protection.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; T cells; breakthrough infection; epitope; immunodiagnostic tool; vaccination; viruses.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A. Sette is a consultant for Gritstone Bio, Flow Pharma, Arcturus Therapeutics, ImmunoScape, CellCarta, Avalia, Moderna, Fortress, and Repertoire. S.C. is a consultant for Avalia. La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) has filed for patent protection for various aspects of SARS-CoV-2 epitope pools design. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cohen K.W., Linderman S.L., Moodie Z., Czartoski J., Lai L., Mantus G., Norwood C., Nyhoff L.E., Edara V.V., Floyd K., et al. Longitudinal analysis shows durable and broad immune memory after SARS-CoV-2 infection with persisting antibody responses and memory B and T cells. Cell Rep Med. 2021;2:100354. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collier A.Y., Brown C.M., McMahan K., Yu J., Liu J., Jacob-Dolan C., Chandrashekar A., Tierney D., Ansel J.L., Rowe M., et al. Immune Responses in Fully Vaccinated Individuals Following Breakthrough Infection with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant in Provincetown, Massachusetts. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.10.18.21265113. Preprint at. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

