Identification of differentially expressed genes and pathways in kidney of ANCA-associated vasculitis by integrated bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 35172670
- PMCID: PMC8856091
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2030755
Identification of differentially expressed genes and pathways in kidney of ANCA-associated vasculitis by integrated bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
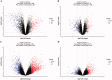
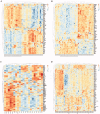
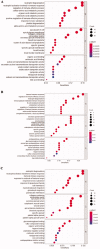
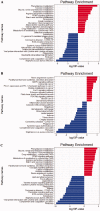
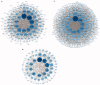
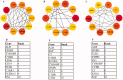
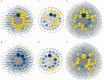
The antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a systematic of relatively rare autoimmune diseases with unknown cause. Kidney involvement is one of the most common clinical manifestations, and the degree of renal damage is closely associated with the development and prognosis of AAV. In this study, we utilized the Robust Rank Aggreg (RRA) method in R to integrate GSE104948, GSE104954, GSE108109, GSE108112, and GSE108113 profile datasets loaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and identified a set of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in kidney between AAV patients and living donors. Then, the results of gene ontology (GO) functional annotation showed that immunity and metabolism involved process of AAV both in glomerulus and tubulointerstitial. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis revealed that following pathways, such as complement and coagulation cascades pathway; Staphylococcus aureus infection; disease-COVID-19; and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathway play a crucial role in AAV. Next, the results analyzed by protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and Cytoscape software exhibited the hub genes ALB, TYROBP, and CYBB existed in both glomerular and tubulointerstitial compartments datasets. Finally, KEGG analysis using genes of two most important modules also further validated complement and coagulation cascades pathway and S. aureus infection existed both in glomerulus and tubulointerstitial compartments datasets. In conclusion, this study identified key genes and pathways involved in kidney of AAV, which was benefit to further uncover the mechanisms underlying the development and progress of AAV, biomarkers, and potential therapeutic targets as well.
Keywords: Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis; Gene Expression Omnibus database; differentially expressed genes; integrated bioinformatics analysis; kidney.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s)
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrated bioinformatic analysis of the shared molecular mechanisms between ANCA-associated vasculitis and atherosclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Dec 19;26(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03448-w. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39702436 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the role of oxidative stress in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis through integrated machine learning and bioinformatics analyses.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2499905. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2499905. Epub 2025 May 14. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40369957 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of Candidate Genes and Pathways Related to Hepatocellular Carcinoma in China: A Study Based on Public Databases.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Mar 26;27:588532. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.588532. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34257537 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring nasopharyngeal carcinoma genetics: Bioinformatics insights into pathways and gene associations.Med J Malaysia. 2024 Sep;79(5):615-625. Med J Malaysia. 2024. PMID: 39352166 Review.
-
[Renal involvement in systemic diseases].Pathologie (Heidelb). 2024 Jul;45(4):261-268. doi: 10.1007/s00292-024-01338-1. Epub 2024 May 28. Pathologie (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38805092 Free PMC article. Review. German.
Cited by
-
The association between serum lipids at diagnosis and renal outcome in microscopic polyangiitis patients.PeerJ. 2025 Feb 10;13:e18839. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18839. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 39950045 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of budesonide on LPS-induced podocyte injury by modulating macrophage M1/M2 polarization: Evidence from in vitro and in silico studies.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jul 26;24(3):589. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11526. eCollection 2022 Sep. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35949344 Free PMC article.
-
Title: Bioinformatic Identification of Genes Involved in Diabetic Nephropathy Fibrosis and their Clinical Relevance.Biochem Genet. 2023 Aug;61(4):1567-1584. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10336-6. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Biochem Genet. 2023. PMID: 36715962
-
Predicting bacterial infection risk in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis in southwest China: development of a new nomogram.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Nov;41(11):3451-3460. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06314-9. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35918562
-
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody‑associated vasculitis complicated with oral and maxillofacial space infection in a young woman: A case report.Exp Ther Med. 2023 May 25;26(1):344. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12043. eCollection 2023 Jul. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37383370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Furuta S, Jayne DR.. Antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis: recent developments. Kidney Int. 2013;84(2):244–249. - PubMed
-
- Cornec D, Cornec-Le Gall E, Fervenza FC, et al. . ANCA-associated vasculitis - clinical utility of using ANCA specificity to classify patients. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(10):570–579. - PubMed
-
- Falk RJ, Jennette JC.. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with specificity for myeloperoxidase in patients with systemic vasculitis and idiopathic necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1988;318(25):1651–1657. - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Yu F, Zhang Y, et al. . Characteristics of chinese patients with wegener's granulomatosis with anti-myeloperoxidase autoantibodies. Kidney Int. 2005;68(5):2225–2229. - PubMed
-
- Mohammad AJ, Jacobsson LT, Mahr AD, et al. . Prevalence of wegener's granulomatosis, microscopic polyangiitis, polyarteritis nodosa and Churg-Strauss syndrome within a defined population in Southern Sweden. Rheumatology. 2007;46(8):1329–1337. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
