Clinicopathological and prognostic value of SIRT6 in patients with solid tumors: a meta-analysis and TCGA data review
- PMID: 35172823
- PMCID: PMC8848894
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02511-3
Clinicopathological and prognostic value of SIRT6 in patients with solid tumors: a meta-analysis and TCGA data review
Abstract
Purposes: In addition to its role in cellular progression and cancer, SIRT6, a member of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent class III deacylase sirtuin family, serves a variety of roles in the body's immune system. In this study, we sought to determine the relationship between the expression of SIRT6 and the clinicopathological outcomes of patients with solid tumours by conducting a meta-analysis of the available data.
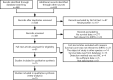
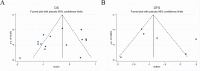
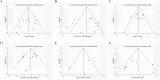
Methods: The databases PubMed and ISI Web of Science were searched for relevant literature, and the results were presented here. Using Stata16.0, a meta-analysis was conducted to determine the impact of SIRT6 on clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis in malignancy patients. The results were published in the journal Cancer Research. The dataset from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) was used to investigate the prognostic significance of SIRT6 in various types of tumors.
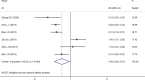
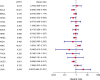
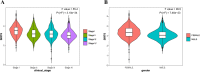
Results: The inclusion and exclusion criteria were met by 15 studies. In patients with solid tumours, reduced SIRT6 expression was found to be related with improved overall survival (OS) (HR = 0.66, 95% CI = 0.45-0.97, P < 0.001) as well as improved disease-free survival (DFS) (HR = 0.48, 95% CI = 0.26-0.91, P < 0.001). Low SIRT6 expression was found to be associated with a better OS in breast cancer (HR = 0.49, 95% CI = 0.27-0.89, P = 0.179), but was found to be associated with a worse OS in gastrointestinal cancer (gastric cancer and colon cancer) (HR = 1.83, 95% CI = 1.20-2.79, P = 0.939) after subgroup analysis. In terms of clinicopathological characteristics, SIRT6 expression was found to be linked with distant metastasis (OR = 2.98, 95% CI = 1.59-5.57, P = 0.694). When the data from the TCGA dataset was compared to normal tissue, it was discovered that SIRT6 expression was significantly different in 11 different types of cancers. Meanwhile, reduced SIRT6 expression was shown to be associated with improved OS (P < 0.05), which was consistent with the findings of the meta-analysis. Aside from that, the expression of SIRT6 was found to be associated with both gender and clinical stage.
Conclusion: The overall data of the present meta-analysis indicated that low expression of SIRT6 may predict a favorable survival for patients with solid tumors.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; Prognosis; SIRT6; Solid tumors.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that no competing of interests existing in this study.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prognostic role of SIRT6 in gastrointestinal cancers: a meta-analysis.Open Med (Wars). 2020 Apr 21;15(1):358-365. doi: 10.1515/med-2020-0403. eCollection 2020. Open Med (Wars). 2020. PMID: 33335996 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic value of epithelial cell adhesion molecule in solid tumours: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 16;13:1242231. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1242231. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37664060 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Long Non-Coding RNA BLACAT1 in Cancer: An Updated Meta-Analysis and TCGA Data Review.Clin Lab. 2020 Nov 1;66(11). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2020.200310. Clin Lab. 2020. PMID: 33180447
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of XPO1 in solid tumors: meta-analysis and TCGA analysis.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2023 Jul-Dec;23(7):607-618. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2023.2224505. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2023. PMID: 37335774 Review.
-
Prognostic value of long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 expression in patients with solid tumors.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Sep;215(9):152449. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152449. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31378453
Cited by
-
The histone deacetylase SIRT6 promotes glycolysis through the HIF-1α/HK2 signaling axis and induces erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer.Apoptosis. 2022 Dec;27(11-12):883-898. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01751-y. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Apoptosis. 2022. PMID: 35915188 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuins as Key Regulators in Pancreatic Cancer: Insights into Signaling Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 6;16(23):4095. doi: 10.3390/cancers16234095. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Multi-Faceted Role of Sirtuins in Glioblastoma Pathogenesis and Targeting Options.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 25;23(21):12889. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112889. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MODILM: towards better complex diseases classification using a novel multi-omics data integration learning model.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 May 5;23(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02173-9. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 37147619 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Sirtuins in the Pathobiology of Onco-Hematological Diseases: A PROSPERO-Registered Study and In Silico Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 23;14(19):4611. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194611. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dong Z, Lei Q, Liu L, Cui H. Function of SIRT6 in tumor initiation and progression. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2016;32(7):870–879. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

