Effects of early-life antibiotics on the developing infant gut microbiome and resistome: a randomized trial
- PMID: 35173154
- PMCID: PMC8850541
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28525-z
Effects of early-life antibiotics on the developing infant gut microbiome and resistome: a randomized trial
Abstract
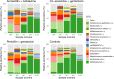
Broad-spectrum antibiotics for suspected early-onset neonatal sepsis (sEONS) may have pronounced effects on gut microbiome development and selection of antimicrobial resistance when administered in the first week of life, during the assembly phase of the neonatal microbiome. Here, 147 infants born at ≥36 weeks of gestational age, requiring broad-spectrum antibiotics for treatment of sEONS in their first week of life were randomized 1:1:1 to receive three commonly prescribed intravenous antibiotic combinations, namely penicillin + gentamicin, co-amoxiclav + gentamicin or amoxicillin + cefotaxime (ZEBRA study, Trial Register NL4882). Average antibiotic treatment duration was 48 hours. A subset of 80 non-antibiotic treated infants from a healthy birth cohort served as controls (MUIS study, Trial Register NL3821). Rectal swabs and/or faeces were collected before and immediately after treatment, and at 1, 4 and 12 months of life. Microbiota were characterized by 16S rRNA-based sequencing and a panel of 31 antimicrobial resistance genes was tested using targeted qPCR. Confirmatory shotgun metagenomic sequencing was executed on a subset of samples. The overall gut microbial community composition and antimicrobial resistance gene profile majorly shift directly following treatment (R2 = 9.5%, adjusted p-value = 0.001 and R2 = 7.5%, adjusted p-value = 0.001, respectively) and normalize over 12 months (R2 = 1.1%, adjusted p-value = 0.03 and R2 = 0.6%, adjusted p-value = 0.23, respectively). We find a decreased abundance of Bifidobacterium spp. and increased abundance of Klebsiella and Enterococcus spp. in the antibiotic treated infants compared to controls. Amoxicillin + cefotaxime shows the largest effects on both microbial community composition and antimicrobial resistance gene profile, whereas penicillin + gentamicin exhibits the least effects. These data suggest that the choice of empirical antibiotics is relevant for adverse ecological side-effects.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.B. declares to have received unrestricted fees paid to the institution for advisory work for Friesland Campina as well as research support from Nutricia. None of the fees or grants listed here was received for the research described in this paper. No other authors report financial disclosures. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Oosterloo BC, et al. Wheezing and infantile colic are associated with neonatal antibiotic treatment. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018;29:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Alm B, et al. Neonatal antibiotic treatment is a risk factor for early wheezing. Pediatrics. 2008;121:697–702. - PubMed
-
- Salvatore S, et al. Neonatal antibiotics and prematurity are associated with an increased risk of functional gastrointestinal disorders in the first year of life. J. Pediatr. 2019;212:44–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

