Cost-Utility Analysis of a Latanoprost Cationic Emulsion (STN1013001) versus Other Latanoprost in the Treatment of Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular Hypertension and Concomitant Ocular Surface Disease in Germany
- PMID: 35173411
- PMCID: PMC8841531
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S351013
Cost-Utility Analysis of a Latanoprost Cationic Emulsion (STN1013001) versus Other Latanoprost in the Treatment of Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular Hypertension and Concomitant Ocular Surface Disease in Germany
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to estimate the cost-utility and economic value of STN1013001, a latanoprost cationic emulsion vs other latanoprost formulations (henceforth latanoprost) in patients with open-angle glaucoma (OAG) or ocular hypertension (OHT) and concomitant ocular surface disease (OSD) in Germany.
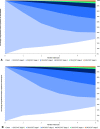
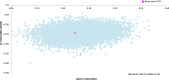
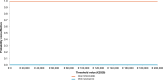
Methods: An early 5-year Markov model-supported cost-utility analysis was performed to estimate costs, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) and life-years saved (LYS) for STN1013001 vs latanoprost from the German health system perspective. The model included seven mutually exclusive health states and adopted a 1-year cycle length. The model was populated with pooled data derived, by means of a questionnaire, from a convenience sample of five German glaucoma specialists. Remaining data were derived from published sources. Data provided by the ophthalmologists included annual treatment adherence probabilities, utility values and resource utilization. The half-cycle correction as well as a discount rate of 3.0% per year were applied to costs (expressed in €2020), life-year saved (LYS) and QALYs. The incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) was contrasted against the informal willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold for incremental LYS saved or QALY gained (€30,000) proposed for Germany. One-way and probabilistic sensitivity analyses (OWSA; PSA) tested the robustness of the base case ICUR.
Results: Over the 5-year time horizon, STN1013001 strongly dominates latanoprost as it is less costly (€1003.65 vs €1145.37; -12.37%) and produces more QALYs (2.612 vs 2.365; +10.44%) per notional patient. Baseline findings were robust against all the variations included in OWSA. PSA shows that STN1013001 has a 100% probability of being cost-effective vs Latanoprost at each WTP threshold for incremental QALY gained.
Conclusion: Once on the market, STN1013001 will provide a cost-effective and possibly strongly dominant therapy vs latanoprost for OAG/OHT+OSD patients from a German health system perspective. Future empirical research should confirm these findings.
Keywords: Germany; STN1013001; cost–utility analysis; latanoprost; ocular surface disease; open-angle glaucoma.
© 2022 Lazzaro et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CL has received an unconditional research grant from Santen GmbH, München, Germany. Outside this research, in the past 3 years CL has received research grants, speaker or consultancy fees from AstraZeneca S.p.A., Boehringer Ingelheim Italia S.p.A., CSL Behring S. p.A., Ferring S.p.A., Ipsen S.p.A., Roche S.p.A., Sanofi s.r.l., Santen GmbH, Shire S.p.A, Sobi S.p.A. CvS and LA are employees of Santen GmbH, München, Germany. SB, HF, CK, SP and UT received research fee for data provision from Santen GmbH, München, Germany. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Lorenz K, Wolfram C, Breitscheidel L, Shlaen M, Verboven Y, Pfeiffer N. Direct cost and predictive factors for treatment in patients with ocular hypertension or early, moderate and advanced primary open-angle glaucoma: the CoGIS study in Germany. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;251(8):2019–2028. doi:10.1007/s00417-013-2354-z - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

