New Insights Into the Epigenetic Regulation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 35173618
- PMCID: PMC8841592
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.813659
New Insights Into the Epigenetic Regulation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
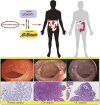
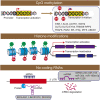
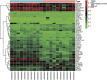
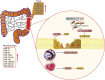
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the colonic mucosa. Environmental factors, genetics, intestinal microbiota, and the immune system are all involved in the pathophysiology of IBD. Lately, accumulating evidence has shown that abnormal epigenetic changes in DNA methylation, histone markers, and non-coding RNA expression greatly contribute to the development of the entire disease. Epigenetics regulates many functions, such as maintaining the homeostasis of the intestinal epithelium and regulating the immune system of the immune cells. In the present study, we systematically summarized the latest advances in epigenetic modification of IBD and how epigenetics reveals new mechanisms of IBD. Our present review provided new insights into the pathophysiology of IBD. Moreover, exploring the patterns of DNA methylation and histone modification through epigenetics can not only be used as biomarkers of IBD but also as a new target for therapeutic intervention in IBD patients.
Keywords: DNA methylation; epigenetics; histone modifications; inflammatory; inflammatory bowel disease; miRNA.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Xu, Yang, Liang, Peng, Zhang, Tian, Wang, Yao, Nie and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adams A. T., Kennedy N. A., Hansen R., Ventham N. T., OʼLeary K. R., Drummond H. E., et al. Two-stage Genome-wide Methylation Profiling in Childhood-Onset Crohn's Disease Implicates Epigenetic Alterations at the VMP1/MIR21 and HLA Loci. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014;20:1784–1793.10.1097/MIB.0000000000000179 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

