Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients With Severe Chronic Heart Failure
- PMID: 35173696
- PMCID: PMC8843083
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.813289
Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients With Severe Chronic Heart Failure
Abstract
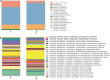
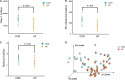
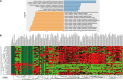
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is the final outcome of almost all forms of cardiovascular diseases, remaining the main cause of mortality worldwide. Accumulating evidence is focused on the roles of gut microbial community in cardiovascular disease, but few studies have unveiled the alterations and further directions of gut microbiota in severe CHF patients. Aimed to investigate this deficiency, fecal samples from 29 CHF patients diagnosed with NYHA Class III-IV and 30 healthy controls were collected and then analyzed using bacterial 16S rRNA gene sequencing. As a result, there were many significant differences between the two groups. Firstly, the phylum Firmicutes was found to be remarkably decreased in severe CHF patients, and the phylum Proteobacteria was the second most abundant phyla in severe CHF patients instead of phylum Bacteroides strangely. Secondly, the α diversity indices such as chao1, PD-whole-tree and Shannon indices were significantly decreased in the severe CHF versus the control group, as well as the notable difference in β-diversity between the two groups. Thirdly, our result revealed a remarkable decrease in the abundance of the short-chain fatty acids (SCFA)-producing bacteria including genera Ruminococcaceae UCG-004, Ruminococcaceae UCG-002, Lachnospiraceae FCS020 group, Dialister and the increased abundance of the genera in Enterococcus and Enterococcaceae with an increased production of lactic acid. Finally, the alternation of the gut microbiota was presumably associated with the function including Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning, Amino acid transport and metabolism and Carbohydrate transport and metabolism through SCFA pathway. Our findings provide the direction and theoretical knowledge for the regulation of gut flora in the treatment of severe CHF.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene; SCFA; gut microbiota; patients; severe chronic heart failure.
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Du, Fu, Han, Li and Ju.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alrafas H. R., Busbee P. B., Chitrala K. N., Nagarkatti M., Nagarkatti P. (2020). Alterations in the gut microbiome and suppression of histone deacetylases by resveratrol are associated with attenuation of colonic inflammation and protection against colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 9:1796. 10.3390/jcm9061796 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

