The molecular mechanism of kinesin family member 2A (KIF2A) underlying non-small cell lung cancer: the effect of its knockdown on malignant behaviors, stemness, chemosensitivity, and potential regulated signaling pathways
- PMID: 35173830
- PMCID: PMC8829653
The molecular mechanism of kinesin family member 2A (KIF2A) underlying non-small cell lung cancer: the effect of its knockdown on malignant behaviors, stemness, chemosensitivity, and potential regulated signaling pathways
Abstract
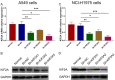
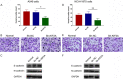
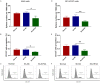
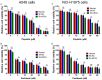
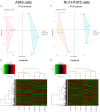
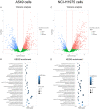
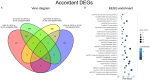
Kinesin family member 2A (KIF2A) represents an oncogene in several cancers, however, its involvement in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is limitedly investigated. Therefore, the present study aimed to explore potential molecular mechanism of KIF2A knockdown in repressing NSCLC malignant behaviors. The effect of KIF2A knockdown on cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers, stemness, chemosensitivity was detected after transfecting KIF2A short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) plasmids into A549 and NCI-H1975 cells. Moreover, KIF2A knockdown mediated signaling pathways were analyzed by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), and then validated by western blot assay. Both KIF2A mRNA and protein expressions were increased in A549, NCI-H650, NCI-H358, NCI-H2106, NCI-H1299, NCI-H1650 and NCI-H1975 cells compared with BEAS-2B cells. KIF2A knockdown inhibited proliferation, invasion, EMT, stemness, but enhanced chemosensitivity to cisplatin and paclitaxel in both A549 and NCI-H1975 cells. Meanwhile, it only promoted apoptosis in NCI-H1975 cells but not in A549 cells. Moreover, after KIF2A knocking down, RNA-seq data indicated that 356 accordant differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in both A549 and NCI-H1975 cells, and these DEGs were enriched in PI3K-Akt, Wnt and Notch signaling pathways. Further western blot disclosed that KIF2A knockdown indeed inactivated PI3K-Akt, Wnt and Notch signaling pathways in both A549 and NCI-H1975 cells. In conclusion, KIF2A knockdown suppresses NSCLC cell malignant behaviors, EMT and stemness, but enhances chemosensitivity via inactivating PI3K-Akt, Wnt, and Notch signaling pathways, which proposes it as a potential therapeutic target for NSCLC treatment.
Keywords: Kinesin family member 2A; RNA-sequencing; chemosensitivity; malignant behaviors; non-small cell lung cancer.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Arbour KC, Riely GJ. Systemic therapy for locally advanced and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a review. JAMA. 2019;322:764–774. - PubMed
-
- Valentino F, Borra G, Allione P, Rossi L. Emerging targets in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2018;14:61–72. - PubMed
-
- Ettinger DS, Aisner DL, Wood DE, Akerley W, Bauman J, Chang JY, Chirieac LR, D’Amico TA, Dilling TJ, Dobelbower M, Govindan R, Gubens MA, Hennon M, Horn L, Lackner RP, Lanuti M, Leal TA, Lilenbaum R, Lin J, Loo BW, Martins R, Otterson GA, Patel SP, Reckamp K, Riely GJ, Schild SE, Shapiro TA, Stevenson J, Swanson SJ, Tauer K, Yang SC, Gregory K, Hughes M. NCCN guidelines insights: non-small cell lung cancer, version 5.2018. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018;16:807–821. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
