Radix Rehmannia Glutinosa inhibits the development of renal fibrosis by regulating miR-122-5p/PKM axis
- PMID: 35173832
- PMCID: PMC8829622
Radix Rehmannia Glutinosa inhibits the development of renal fibrosis by regulating miR-122-5p/PKM axis
Abstract
Objective: It is acknowledged that Radix Rehmanniae Praeparata (RR) can regulate hormone metabolism, reduce blood glucose, resist aging, help to sedate patients and promote diuresis. The study aims to investigate the mechanism of how RR influences the development of renal fibrosis by regulating the miR-122-5p/PKM axis.
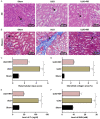
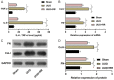
Methods: Unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) was applied to induce renal fibrosis in mice in vivo, and human tubular epithelial HK2 cells treated by transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β1) were used to induce renal fibrosis in vitro. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in mouse serum were detected by Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); fibronectin (FN) and type I collagen (Col-I) in renal tissue were detected by Western blotting; serum creatinine (Cr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were analyzed by kits. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining and Masson staining were utilized to assess the degree of pathological damage and fibrosis. Cell viability and apoptosis in the in vitro model were detected by MTT and Flow cytometry. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to determine intermolecular targeting relationships.
Results: RR could inhibit IL-6 and TNF-α levels, decrease the levels of FN and Col-I and improve the renal function indexes (serum Cr and BUN) in UUO mice (all P<0.05). In addition, RR was able to promote the up-regulation of miR-122-5p expression in UUO mice in vivo (P<0.05). MiR-122-5p expression was down-regulated and PKM expression was up-regulated in HK2 cells treated with TGF-β1 (all P<0.05). RR inhibited renal fibrosis progression by regulating the miR-122-5p/PKM axis. Inhibition of miR-122-5p or overexpression of PKM could promote apoptosis of TGF-β1-treated HK2 cells, inhibit their viability, aggravate fibrosis, and attenuate the protective effect of RR on the cells. The protective effect of RR promoted by overexpression of miR-122-5p was partially counteracted by PKM.
Conclusion: RR can inhibit renal fibrosis progression by regulating the miR-122-5p/PKM axis.
Keywords: PKM; Radix Rehmannia Glutinosa; miR-122-5p; renal fibrosis.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Rehmanniae Radix and Rehmanniae Radix Praeparata Ameliorates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis Induced by Unilateral Ureteral Occlusion in Rats and Their Mechanism].Zhong Yao Cai. 2015 Dec;38(12):2507-10. Zhong Yao Cai. 2015. PMID: 27352530 Chinese.
-
Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch and Cornus officinalis Sieb herb couple ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis in CKD rats by inhibiting the TGF-β1/MAPK signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt B):117039. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117039. Epub 2023 Aug 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37579922
-
CircRNA circ-ITCH improves renal inflammation and fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by regulating the miR-33a-5p/SIRT6 axis.Inflamm Res. 2021 Jul;70(7):835-846. doi: 10.1007/s00011-021-01485-8. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34216220
-
Puerarin alleviates chronic renal failure-induced pyroptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells by targeting miR-342-3p/TGF-β/SMAD axis.Genes Genomics. 2023 Dec;45(12):1563-1573. doi: 10.1007/s13258-023-01448-9. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Genes Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37747643
-
Rehmanniae Radix, an Effective Treatment for Patients with Various Inflammatory and Metabolic Diseases: Results from a Review of Korean Publications.J Pharmacopuncture. 2017 Jun;20(2):81-88. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2017.20.010. Epub 2017 Jun 30. J Pharmacopuncture. 2017. PMID: 30087783 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heidihuangwan alleviates renal fibrosis in rats with 5/6 nephrectomy by inhibiting autophagy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 9;13:977284. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.977284. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160409 Free PMC article.
-
The Inhibition of Fibrosis and Inflammation in Obstructive Kidney Injury via the miR-122-5p/SOX2 Axis Using USC-Exos.Biomater Res. 2024 Apr 10;28:0013. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0013. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 38617751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg P, Jeppesen M, Leipziger J. Cystic fibrosis in the kidney: new lessons from impaired renal HCO3-excretion. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2021;30:437–443. - PubMed
-
- Mylonas KJ, O’Sullivan ED, Humphries D, Baird DP, Docherty MH, Neely SA, Krimpenfort PJ, Melk A, Schmitt R, Ferreira-Gonzalez S, Forbes SJ, Hughes J, Ferenbach DA. Cellular senescence inhibits renal regeneration after injury in mice, with senolytic treatment promoting repair. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13:eabb0203. - PubMed
-
- Gao Y, Yuan D, Gai L, Wu X, Shi Y, He Y, Liu C, Zhang C, Zhou G, Yuan C. Saponins from panax japonicus ameliorate age-related renal fibrosis by inhibition of inflammation mediated by NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad signaling and suppression of oxidative stress via activation of Nrf2-ARE signaling. J Ginseng Res. 2021;45:408–419. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doke T, Huang S, Qiu C, Liu H, Guan Y, Hu H, Ma Z, Wu J, Miao Z, Sheng X, Zhou J, Cao A, Li J, Kaufman L, Hung A, Brown CD, Pestell R, Susztak K. Transcriptome-wide association analysis identifies DACH1 as a kidney disease risk gene that contributes to fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2021;131:e141801. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Wu C, Xu M, Cheng C, Liu Y, Di X. Optimisation for simultaneous determination of iridoid glycosides and oligosaccharides in radix rehmannia by microwave assisted extraction and HILIC-UHPLC-TQ-MS/MS. Phytochem Anal. 2020;31:340–348. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
