circ_014260/miR-384/THBS1 aggravates spinal cord injury in rats by promoting neuronal apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 35173872
- PMCID: PMC8829636
circ_014260/miR-384/THBS1 aggravates spinal cord injury in rats by promoting neuronal apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
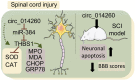
Objective: To explore the mechanism of circ_014260 regulating neuronal apoptosis, oxidative stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with spinal cord injury (SCI) via miR-384/THBS1 axis.
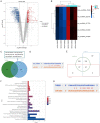
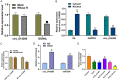
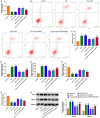
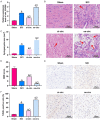
Methods: T9-L10 spinal cord segments of Sprague Dawley rats were subjected to compression or contusion injuries after T10 laminectomy to establish rat models of SCI, which were then divided into SCI group, si-circ group and oe-circ group according to the transfection. There was another sham operation group which received no treatment. There were 10 rats in each group. The Basso-Beattie-Bresnahan scale and HE staining were used to evaluate the changes in neuronal motor function in rats with SCI. TUNEL staining was used to determine the neuronal apoptosis. Flow cytometry was used to measure the changes in H2O2-induced apoptosis of primary neurons. The activities of myeloperoxidase, malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase and catalase were measured to evaluate the level of oxidative stress. Western blot was used to measure the expressions of CHOP and CRP78 (which are related to endoplasmic reticulum stress). Expression of circ_014260, miR-384 and THBS1 in tissues and cells was measured by qRT-PCR. RNase R restriction enzyme digestion and chromatin fractionation were used to identify the nature of circ_014260. Dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation were used to verify the targeted binding relationship between circ_014260 and miR-384, as well as between miR-384 and THBS1.
Results: Compared with the sham operation group or the untreated rat primary neurons (control group), increased expression of circ_014260 and THBS1 as well as decreased expression of miR-384 were observed in the spinal cord tissue from rats with SCI and in H2O2-treated primary neurons (all P<0.05). The results of both in vivo and in vitro experiments showed that knocking down circ_014260 could reduce neuronal apoptosis and inhibit oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with SCI (all P<0.05). Circ_014260 targetedly inhibited miR-384 to up-regulate the expression of THBS1. Both miR-384 inhibitor and THBS1 overexpression vector partially reversed the alleviated neuronal damage by knocking down circ_014260 (both P<0.05).
Conclusion: Circ_014260 promotes neuronal damage in rats with SCI by inhibiting miR-384 to up-regulate the expression of THBS1. Thus, circ_014260 could possibly be a new molecular target of SCI.
Keywords: THBS1; circ_014260; miR-384; spinal cord injury.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Circ-KATNAL1 Knockdown Reduces Neuronal Apoptosis and Alleviates Spinal Cord Injury Through the miR-98-5p/PRDM5 Regulatory Axis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Oct;66(10):2841-2849. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00895-9. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37758970
-
Nerve growth factor improves functional recovery by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal apoptosis in rats with spinal cord injury.J Transl Med. 2014 May 15;12:130. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-130. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 24884850 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-34a Inhibits Spinal Cord Injury and Blocks Spinal Cord Neuron Apoptosis by Activating Phatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT Pathway Through Targeting CD47.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2019;16(4):373-381. doi: 10.2174/1567202616666190906102343. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 31490756
-
MiR-124 inhibits spinal neuronal apoptosis through binding to GCH1.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jun;23(11):4564-4574. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201906_18032. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31210282
-
The effect of metformin on ameliorating neurological function deficits and tissue damage in rats following spinal cord injury: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 11;16:946879. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.946879. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36117612 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
mRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA expression profiles in a new aortic dissection murine model induced by hypoxia and Ang II.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 26;9:984087. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.984087. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36386298 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Transplantation/Transfer: Promising Therapeutic Strategies for Spinal Cord Injury.J Orthop Translat. 2025 May 16;52:441-450. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.04.017. eCollection 2025 May. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 40485848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circ-KATNAL1 Knockdown Reduces Neuronal Apoptosis and Alleviates Spinal Cord Injury Through the miR-98-5p/PRDM5 Regulatory Axis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Oct;66(10):2841-2849. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00895-9. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37758970
-
THBS1 in macrophage-derived exosomes exacerbates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inducing ferroptosis in endothelial cells.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Feb 24;22(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03382-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 39994679 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA DANCR increases spinal cord neuron apoptosis and inflammation of spinal cord injury by mediating the microRNA-146a-5p/MAPK6 axis.Eur Spine J. 2024 May;33(5):2056-2067. doi: 10.1007/s00586-024-08216-7. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 38551688
References
-
- Jasim M, Brindha T. Spinal cord segmentation and injury detection using a crow search-rider optimization algorithm. Biomed Tech (Berl) 2021;66:293–304. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Fu B, Bao J, Su R, Zhao H, Liu Z. Novel circular RNA 2960 contributes to secondary damage of spinal cord injury by sponging miRNA-124. J Comp Neurol. 2021;529:1456–1464. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
