Effect of various doses of rosuvastatin in the treatment of elderly patients with unstable angina pectoris
- PMID: 35173877
- PMCID: PMC8829618
Effect of various doses of rosuvastatin in the treatment of elderly patients with unstable angina pectoris
Abstract
Objectives: This prospective study aimed to explore the effects of various doses of rosuvastatin on the hemodynamic changes, highly sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in elderly patients with unstable angina pectoris.
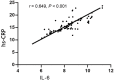
Methods: One-hundred and six elderly patients with unstable angina pectoris were enrolled and divided into group A (n=55) and group B (n=51). Under the same treatment for angina pectoris, patients in groups A and B were administered with 5 mg and 10 mg of rosuvastatin orally once every night, respectively. The two groups were compared in terms of hemorheology, coagulation indices and immune reaction (serum hs-CRP and IL-6 levels), changes of clinical indices, electrocardiograph (ECG), therapeutic effect, and incidence of adverse reactions. Serum hs-CRP and IL-6 levels were detected by ELISA method, and their correlation was analyzed by Pearson method.
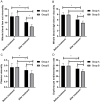
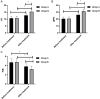
Results: Whole blood viscosity at high cut (BVH), whole blood viscosity at low cut (BVL), plasma viscosity (PV), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), immunoglobulin index, and the hs-CRP and IL-6 levels decreased in both groups after treatment and were lower in group B than in group A (P<0.05). Prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) increased, while fibrinogen (FIB) decreased in both groups after treatment (P<0.05). Group B was superior to group A in the onset times of myocardial ischemia and angina pectoris, the total duration of myocardial ischemia, and the total effective rate indicated by ECG (P<0.05). No statistical difference was observed in the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups after treatment (P>0.05).
Conclusions: The optimal efficacy of rosuvastatin at 10 mg/day was higher than that of rosuvastatin at 5 mg/day.
Keywords: IL-6; Various doses; elderly patients; hs-CRP; rosuvastatin; unstable angina pectoris.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Relevant detection indicator of prethrombotic state in patients with primary hypertension.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Aug 26;11(24):5678-5691. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i24.5678. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37727711 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between Changes in Serum RBP4, hs-CRP, and IL-27 Levels and Rosuvastatin in the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Dec 15;2021:8476592. doi: 10.1155/2021/8476592. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 34956579 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Analysis of Acute Coronary Syndrome with Serum IL-18, MMP-9, hs-CRP, and Plasma FIB.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jan 4;2022:5984184. doi: 10.1155/2022/5984184. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2024 Mar 20;2024:9824926. doi: 10.1155/2024/9824926. PMID: 35028315 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and safety of sodium tanshinone ⅡA sulfonate injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 31;18(8):e0290841. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290841. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37651454 Free PMC article.
-
Dazhu Hongjingtian Preparation as Adjuvant Therapy for Unstable Angina Pectoris: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 10;11:213. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00213. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32210811 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prescribing Renally Inappropriate Medication to Hospitalized Geriatric Patients in Makkah, Saudi Arabia.Int J Gen Med. 2024 May 1;17:1755-1764. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S462135. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38706746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tresukosol D, Sriyudhasak O, Panchavinnin P, Phankingthongkum R. Nadroparin and percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty in elderly thais with unstable angina. Applied Catalysis A General. 2005;159:241–258.
-
- Hong MK. S22-1 comparison of coronary plaque rupture between stable angina and acute myocardial infarction: a three-vessel intravascular ultrasound study in 235 patients. CVD Prevention and Control. 2009:S33–S34. - PubMed
-
- Mintz GS, Maehara A, Bui AB, Weissman NJ. Multiple versus single coronary plaque ruptures detected by intravascular ultrasound in stable and unstable angina pectoris and in acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2003;91:1333. - PubMed
-
- Pelter MM, Loranger DL, Kozik TM, Kedia A, Ganchan RP, Ganchan D, Hu X, Carey MG. Among unstable angina and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients, transient myocardial ischemia and early invasive treatment are predictors of major in-hospital complications. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2016;31:E10–19. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Han X, Jeong MH, Sim DS, Kim MC, Kim Y, Kim JH, Hong YJ, Ahn Y. Successful treatment of coronary spasm with atherosclerosis rapidly progressing to acute myocardial infarction in a young woman. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2018;7:68–75.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
