Rectal administration of Panax notoginseng and Colla Corii Asini suppositories in ulcerative colitis: clinical effect and influence on immune function
- PMID: 35173878
- PMCID: PMC8829602
Rectal administration of Panax notoginseng and Colla Corii Asini suppositories in ulcerative colitis: clinical effect and influence on immune function
Abstract
Objective: This study was designed to evaluate the efficacy of rectal administration of different doses of Panax notoginseng and Colla Corii Asini (CCA) suppositories in the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC) and the effect on immune function and recurrence.
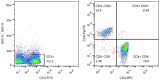
Methods: Totally 120 UC patients admitted to our hospital from February 2019 to February 2020 were enrolled and randomized into experimental group (n=60) and control group (n=60). The experimental group received rectal administration of a high dose of Panax notoginseng and CCA suppositories, while the control group received a low dose. After three months of treatment, clinical symptom scores, inflammatory factor levels, scores of rectal mucosa, immune function, recurrence rates, adverse reaction rates, and clinical efficacy were compared between the two groups.
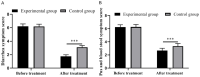
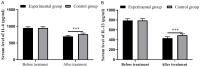
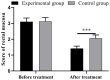
Results: After treatment, the experimental group obtained significantly lower clinical symptom scores, inflammatory factors, and scores of rectal mucosa than the control group (all P<0.001). The immune function of the observation group was significantly better than that of the control group (P<0.001). At 6, 8, and 12 months after treatment, the recurrence rates in the experimental group were all significantly lower than those in the control group (all P<0.001). The two groups showed no significant difference in the incidence of adverse reaction (P>0.05), and the experimental group obtained a higher clinical efficacy than the control group (P<0.001).
Conclusion: For patients with UC, the rectal administration of Panax notoginseng and CCA suppositories can exert positive effects on their inflammatory factors, immune functions, UC severity, clinical symptoms, and recovery. In addition, higher doses were associated with better effects without increased adverse events.
Keywords: Panax notoginseng and Colla Corii Asini suppositories; rectal administration; ulcerative colitis.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of the Panax Notoginseng Ejiao Suppository in the Treatment of Patients with Ulcerative Proctitis and Its Effect on Inflammatory Response and Immune Function.Dis Markers. 2022 Sep 21;2022:1479964. doi: 10.1155/2022/1479964. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. Retraction in: Dis Markers. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9793517. doi: 10.1155/2023/9793517. PMID: 36188425 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Antibacterial activity and effects of Colla corii asini on Salmonella typhimurium invasion in vitro and in vivo.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Dec 4;17(1):520. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-2020-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 29202825 Free PMC article.
-
[A multiplex PCR method based on nuclear and cytoplasmic inheritance to identify the horse and donkey-derived components of Asini Colla Corii and the hide].Yi Chuan. 2020 Oct 20;42(10):1028-1035. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-108. Yi Chuan. 2020. PMID: 33229327 Chinese.
-
Review of normal gastrointestinal tract, ulcerative colitis, proctitis and rectal medication adherence.Br J Nurs. 2020 Jul 23;29(14):805-811. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2020.29.14.805. Br J Nurs. 2020. PMID: 32697644 Review.
-
Rectal budesonide and mesalamine formulations in active ulcerative proctosigmoiditis: efficacy, tolerance, and treatment approach.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2016 May 19;9:125-30. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S80237. eCollection 2016. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27274301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pulchinenoside B4 ameliorates oral ulcers in rats by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 9;108(1):292. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13099-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38592514 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological effects of ginseng and ginsenosides on intestinal inflammation and the immune system.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 18;15:1353614. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1353614. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38698858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network analysis and in vivo experiments reveal the therapeutic mechanisms of total ginsenosides in a Drosophila model of ulcerative colitis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 25;16:1556579. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1556579. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40201696 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary medicines and ginseng for inflammatory bowel disease-rooted in science, but will it bear fruit?World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 21;31(27):108524. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.108524. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40741107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Graziano F, Macaluso FS, Cassata N, Citrano M, Orlando A. Pyoderma gangrenosum in an UC pediatric patient during vedolizumab therapy successfully treated with oral cyclosporine. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27:e110–e111. - PubMed
-
- Bossuyt P, Vermeire S, Bisschops R. Assessing disease activity in UC using artificial intelligence: can “equally good” be seen as “better”? Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1625–1626. - PubMed
-
- Fudman DI, Sattler L, Feuerstein JD. Inpatient management of acute severe UC. J Hosp Med. 2019;14:766–773. - PubMed
-
- Kotwani P, Terdiman J, Lewin S. Tofacitinib for rescue therapy in acute severe uc: a real-world experience. J Crohns Colitis. 2020;14:1026–1028. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
