Comprehensive Analysis of Circular RNA Expression in ceRNA Networks and Identification of the Effects of hsa_circ_0006867 in Keloid Dermal Fibroblasts
- PMID: 35174214
- PMCID: PMC8841745
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.800122
Comprehensive Analysis of Circular RNA Expression in ceRNA Networks and Identification of the Effects of hsa_circ_0006867 in Keloid Dermal Fibroblasts
Abstract
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of various fibrotic diseases, but the potential biological function and expression profile of circRNAs in keloids remain unknown. Herein, microarray technology was applied to detect circRNA expression in four patient-derived keloid dermal fibroblasts (KDFs) and normal dermal fibroblasts (NDFs). A total of 327 differentially expressed (DE) circRNAs (fold change > 1.5, p < 0.05) were identified with 195 upregulated and 132 downregulated circRNAs. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses showed that the upregulated circRNAs were mainly enriched in the cytoskeleton and tight junctions, while the downregulated circRNAs were related to morphogenesis of the epithelium and axonal guidance. To explore the function of DE circRNAs, a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network, including five circRNAs, nine miRNAs, and 235 correlated mRNAs, was constructed using bioinformatics analyses. The expression of five DE circRNAs was validated by qRT-PCR in 18 pairs of KDFs and NDFs, and hsa_circ_0006867 showed promising regulatory function in keloids in vitro. Silencing hsa_circ_00006867 suppressed the proliferation, migration, and invasion of keloid fibroblasts. RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays indicated that hsa_circ_00006867 may serve as a platform for miRNA binding to Argonaute (AGO) 2. In addition, hsa-miR-29a-5p may be a potential target miRNA of hsa_circ_00006867. Taken together, our research provided multiple novel clues to understand the pathophysiologic mechanism of keloids and identified hsa_circ_0006867 as a biomarker of keloids.
Keywords: ceRNA network; circular RNA; dermal fibroblast; keloid; miRNA sponge; microarray analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Pang, Lin, Sun, Hu, Dai, Shen, Xu and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




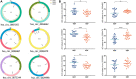

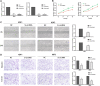

References
-
- Dong Z.-R., Ke A.-W., Li T., Cai J.-B., Yang Y.-f., Zhou W., et al. (2021). CircMEMO1 Modulates the Promoter Methylation and Expression of TCF21 to Regulate Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Sorafenib Treatment Sensitivity. Mol. Cancer 20 (1), 75. 10.1186/s12943-021-01361-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

