Usefulness of four surrogate indexes of insulin resistance in middle-aged population in Hefei, China
- PMID: 35175162
- PMCID: PMC8856080
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2039956
Usefulness of four surrogate indexes of insulin resistance in middle-aged population in Hefei, China
Abstract
Objective: Previous study have shown that lipid accumulation product (LAP), visceral adiposity index (VAI), triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (TG/HDL-C) and triglycerides/glucose index (TyG index) could be simple clinical indicators of insulin resistance (IR) based on anthropometric and/or biochemical parameters. However, the rational and preferred surrogate marker of IR in different population has yet to be validated. The aim of this study was evaluating the practicability of the LAP, VAI, TG/HDL-C, and TyG in predicting IR in middle-aged Chinese population.
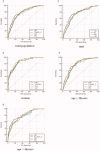
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in 569 Chinese participants (mean age was 48.5; man 67.7%), and each participant completed a questionnaire survey, anthropometric measurement, and biochemical testing. One-way ANOVAs, Chi-squared test, Pearson's correlation, and multiple logistic regression were used to evaluate the association between VAI, LAP, TG/HDL-C, and TyG with IR. To correctly discriminate individuals with insulin resistance, a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was conducted for each evaluated variable and the overall diagnostic accuracy was quantified using the area under the ROC curve (AUC). The AUC of evaluated variables were compared using a nonparametric approach. The optimal cut-off points were determined by the Youden's index, and the corresponding sensitivity and specificity were provided.
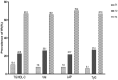
Results: Significant positive correlation was identified between HOMA-IR with TG/HDL-C (r = 0.306), VAI (r = 0.217), LAP (r = 0.381), and TyG (r = 0.371), respectively (all p < .001). After adjustment for potential confounders of IR, compared with the lowest tertiles, odds ratio (95% CI) having IR in the highest tertiles of TG/HDL-C, VAI, LAP and TyG were 6.07 (2.89-12.71), 10.89 (4.37-27.13), 4.68 (2.00-10.92), and 12.20 (5.04-29.56). The area under ROC curves to predict HOMA-diagnosed IR was 0.773 for TG/HDL-C, 0.767 for VAI, 0.806 for LAP, and 0.800 for TyG, respectively. Among those, LAP showed the greatest value of AUC [0.806 (0.763-0.850)] and highest specificity (0.804).
Conclusion: Compared with other indicators, the LAP and TyG are simple, relatively accurate, clinically available surrogate markers of insulin resistance in middle-aged population in Hefei, China. Among 4 evaluated parameters, the LAP have the highest specificity and the TyG have the highest sensitivity.Key MessagesLAP and TyG could be used as simple and alternative methods to identify the individuals at risk for insulin resistance.LAP and TyG have relatively high predictive ability in diagnosis of IR compared with VAI and TG/HDL-C.No significant difference is observed between LAP and TyG in the ability of predicting insulin resistance.
Keywords: Insulin resistance; lipid parameters; odds ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipid accumulation product and triglycerides/glucose index are useful predictors of insulin resistance.J Diabetes Complications. 2018 Mar;32(3):266-270. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Oct 21. J Diabetes Complications. 2018. PMID: 29395839
-
Clinical usefulness of lipid ratios, visceral adiposity indicators, and the triglycerides and glucose index as risk markers of insulin resistance.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Oct 20;13:146. doi: 10.1186/s12933-014-0146-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 25326814 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride Glucose-Body Mass Index Is a Simple and Clinically Useful Surrogate Marker for Insulin Resistance in Nondiabetic Individuals.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 1;11(3):e0149731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149731. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26930652 Free PMC article.
-
Association of insulin resistance surrogate indices and erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Nov 19;22(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01317-4. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39563412 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the association between insulin resistance surrogate indices and bone mineral density.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 18;15:1499479. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1499479. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39744182 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Establishment and Validation of a New Predictive Model for Insulin Resistance based on 2 Chinese Cohorts: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Endocrinol. 2022 Oct 17;2022:8968793. doi: 10.1155/2022/8968793. eCollection 2022. Int J Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36299856 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Non-insulin-Based Insulin Resistance Indices and Increased Arterial Stiffness Measured by the Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index in Non-hypertensive Chinese Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jul 5;9:903307. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.903307. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35865388 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of seven surrogate insulin resistance indexes for predicting the prevalence of carotid atherosclerosis in normal-weight individuals.Front Public Health. 2023 Aug 31;11:1241523. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1241523. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37719743 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between the Variability of Different Obesity Indices and Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study Based on Populations in Taiwan.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Sep 12;16:2791-2802. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S425198. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37720422 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental exposure to lead and cadmium are associated with triglyceride glucose index.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 30;14(1):2496. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52994-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38291186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lebovitz HE. Insulin resistance: definition and consequences. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001;109(Suppl 2):S135–S148. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E.. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991;14(3):173–194. - PubMed
-
- Adnan E, Rahman IA, Faridin HP.. Relationship between insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome components and serum uric acid. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13(3):2158–2162. - PubMed
-
- Suf M, Z M, J A, et al. . Relationship among obesity, blood lipids and insulin resistance in Bangladeshi adults. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13:444–449. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R.. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979;237(3):E214–E223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
