Attenuation of osteoarthritis progression through intra-articular injection of a combination of synovial membrane-derived MSCs (SMMSCs), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and conditioned medium (secretome)
- PMID: 35177103
- PMCID: PMC8851803
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-021-02851-2
Attenuation of osteoarthritis progression through intra-articular injection of a combination of synovial membrane-derived MSCs (SMMSCs), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and conditioned medium (secretome)
Abstract
Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) as a progressive destructive disease of articular cartilage is the most common joint disease characterized by reduction of joint cartilage thickness, demolition of cartilage surface and new bone formation. To overcome these problems, the purpose of the current research was to evaluate and compare the in vivo effects of synovial membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cell (SMMSCs), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and conditioned medium (secretome) on collagenase II-induced rat knee osteoarthritis (KOA) remedy.
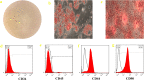
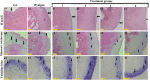
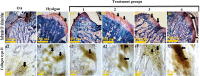
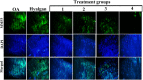
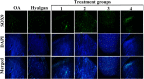
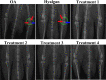
Methods: For the first step, SMMSCs were isolated and characterized. Also, secretome was collected from SMMSCs culture. Furthermore, PRP was collect from the rat heart venous blood. Second, two injection of collagenase II with an interval of 3 days was performed in the knee intra-articular space to induce osteoarthritis. Two weeks later, animals were randomly divided into 6 groups. Control group without treatment, positive group: taken an intra-articular sodium hyaluronate injection (0.1 ml), treatment groups taken an intra-articular injection of; treatment 1: SMMSCs (5 × 106), treatment 2: SMMSCs (5 × 106)/secretome (50 µl), treatment 3: SMMSCs (5 × 106)/PRP (50 µl), and treatment 4: SMMSCs (5 × 106)/ secretome (50 µl)/ PRP (50 µl). Three months later, rats were killed and the following assessments were executed: radiography, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry.
Results: Our findings represented that a combination of the SMMSCs/secretome/PRP had a considerable effect on glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and collagen II contents, articular cartilage preservation, compared with other groups. In addition, combination of the SMMSCs with PRP and secretome showed the lowest expression of mmp3, while SOX9 had the highest expression in comparison with other groups. Also, SMMSCs-injected groups demonstrated better results compared with positive and control groups.
Conclusions: Injecting a combination of the SMMSCs/secretome/PRP resulted in better efficacy in terms of joint space width, articular cartilage surface continuity and integrity, sub-chondral bone and ECM constituents such as collagen II. Indeed, transplantation of this combination could be considered as a preliminary therapy for clinical trial study in the future.
Keywords: Mesenchymal stem cells; Osteoarthritis; PRP; Rat; Secretome.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined with Physical Therapy on IL-1β, TGF-β1, and MMP-3 in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 May;67(5):1991-2001. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01177-8. Epub 2024 May 21. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38771422
-
Comparison of clinical outcome, cartilage turnover, and inflammatory activity following either intra-articular or a combination of intra-articular with intra-osseous platelet-rich plasma injections in osteoarthritis knee: A randomized, clinical trial.Injury. 2023 Feb;54(2):728-737. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.11.036. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Injury. 2023. PMID: 36414504 Clinical Trial.
-
Multiple Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections Versus Single Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Early Osteoarthritis of the Knee: An Experimental Study in a Guinea Pig Model of Early Knee Osteoarthritis.Am J Sports Med. 2019 Aug;47(10):2300-2307. doi: 10.1177/0363546519856605. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Am J Sports Med. 2019. PMID: 31268737
-
Intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma in patients with hemophilia and painful knee joint cartilage degeneration.Expert Rev Hematol. 2023 Jun;16(6):407-416. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2023.2166922. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Expert Rev Hematol. 2023. PMID: 36609192 Review.
-
Effects and safety of the combination of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Apr 11;21(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03262-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32278352 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Intraoperative Platelet-Rich Plasma After Meniscal Repair: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Indian J Orthop. 2024 May 8;58(7):845-857. doi: 10.1007/s43465-024-01155-x. eCollection 2024 Jul. Indian J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38948373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orthobiologics in knee osteoarthritis, dream or reality?Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Sep;144(9):3937-3946. doi: 10.1007/s00402-024-05310-9. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 38630251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) modulate MMP9 expression and promote articular cartilage regeneration in knee joint of a model of arthritis induced in adult rat: histological and immunohistochemical study.J Mol Histol. 2024 Dec 11;56(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10284-4. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39661261
-
Physicochemical and Biological Modifications in Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Conditioned Media Under Hypoxic Preconditioning: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Nanoparticle Stability.Life (Basel). 2025 Apr 26;15(5):702. doi: 10.3390/life15050702. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430131 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the therapeutic potential of infrapatellar fat pad adipose-derived stem cells and their secretome for regenerating knee articular cartilage in a rat model of osteoarthritis.Iran J Vet Res. 2024;25(1):33-40. doi: 10.22099/IJVR.2024.47870.6959. Iran J Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39156795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gupta A, Maffulli N, Rodriguez HC, Mistovich RJ, Delfino K, Cady C, et al. Cell-free stem cell-derived extract formulation for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a preliminary non-randomized, open-label, multi-center feasibility and safety study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):1–7. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02672-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bąkowski P, Kaszyński J, Wałecka J, Ciemniewska-Gorzela K, Bąkowska-Żywicka K, Piontek T. Autologous adipose tissue injection versus platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, controlled study–study protocol. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03345-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

