Attenuation of osteoarthritis progression through intra-articular injection of a combination of synovial membrane-derived MSCs (SMMSCs), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and conditioned medium (secretome)
- PMID: 35177103
- PMCID: PMC8851803
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-021-02851-2
Attenuation of osteoarthritis progression through intra-articular injection of a combination of synovial membrane-derived MSCs (SMMSCs), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and conditioned medium (secretome)
Abstract
Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) as a progressive destructive disease of articular cartilage is the most common joint disease characterized by reduction of joint cartilage thickness, demolition of cartilage surface and new bone formation. To overcome these problems, the purpose of the current research was to evaluate and compare the in vivo effects of synovial membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cell (SMMSCs), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and conditioned medium (secretome) on collagenase II-induced rat knee osteoarthritis (KOA) remedy.
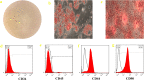
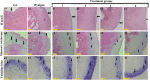
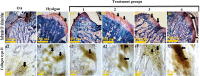
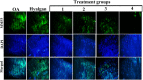
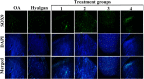
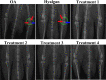
Methods: For the first step, SMMSCs were isolated and characterized. Also, secretome was collected from SMMSCs culture. Furthermore, PRP was collect from the rat heart venous blood. Second, two injection of collagenase II with an interval of 3 days was performed in the knee intra-articular space to induce osteoarthritis. Two weeks later, animals were randomly divided into 6 groups. Control group without treatment, positive group: taken an intra-articular sodium hyaluronate injection (0.1 ml), treatment groups taken an intra-articular injection of; treatment 1: SMMSCs (5 × 106), treatment 2: SMMSCs (5 × 106)/secretome (50 µl), treatment 3: SMMSCs (5 × 106)/PRP (50 µl), and treatment 4: SMMSCs (5 × 106)/ secretome (50 µl)/ PRP (50 µl). Three months later, rats were killed and the following assessments were executed: radiography, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry.
Results: Our findings represented that a combination of the SMMSCs/secretome/PRP had a considerable effect on glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and collagen II contents, articular cartilage preservation, compared with other groups. In addition, combination of the SMMSCs with PRP and secretome showed the lowest expression of mmp3, while SOX9 had the highest expression in comparison with other groups. Also, SMMSCs-injected groups demonstrated better results compared with positive and control groups.
Conclusions: Injecting a combination of the SMMSCs/secretome/PRP resulted in better efficacy in terms of joint space width, articular cartilage surface continuity and integrity, sub-chondral bone and ECM constituents such as collagen II. Indeed, transplantation of this combination could be considered as a preliminary therapy for clinical trial study in the future.
Keywords: Mesenchymal stem cells; Osteoarthritis; PRP; Rat; Secretome.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gupta A, Maffulli N, Rodriguez HC, Mistovich RJ, Delfino K, Cady C, et al. Cell-free stem cell-derived extract formulation for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a preliminary non-randomized, open-label, multi-center feasibility and safety study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):1–7. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02672-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bąkowski P, Kaszyński J, Wałecka J, Ciemniewska-Gorzela K, Bąkowska-Żywicka K, Piontek T. Autologous adipose tissue injection versus platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, controlled study–study protocol. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03345-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

