Measuring quality of life of patients with axial spondyloarthritis for economic evaluation
- PMID: 35177554
- PMCID: PMC8860088
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001955
Measuring quality of life of patients with axial spondyloarthritis for economic evaluation
Abstract
Objectives: To estimate the relationship between EQ5D (three levels, UK version) and the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) for use in the economic evaluation of health technologies for people with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). To compare against the relationship with the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI).
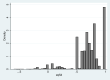
Methods: An electronic, prospective, Portuguese, nationwide, rheumatic disease register (Reuma.pt) provided data on 1140 patients (5483 observations) with a confirmed diagnosis of axSpA. We estimated models of EQ5D as a function of ASDAS, alone or in combination with measures of functional impairment, using bespoke mixture models which reflect the complex distributional features of EQ5D. The SPondyloArthritis Caught Early cohort provided data from 344 patients (1405 observations) in four European countries and was used for validation. A previously published model of BASDAI/Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI) was also used to generate predicted EQ5D scores and model performance compared.
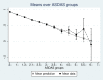
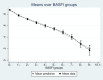
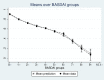
Results: A non-linear relationship exists between EQ5D from ASDAS. The final model included ASDAS, ASDAS squared, age and age squared and demonstrated close fit in both datasets except where data were sparse for patients with very high levels of disease activity (ASDAS >4). This finding held in the validation dataset. Models that included BASFI improved model fit. The ASDAS based models fit the data marginally less well than models using BASDAI.
Conclusions: Mapping models linking ASDAS to EQ5D allow results from clinical studies to be used in economic evaluation of health technologies with confidence. There is some loss of information compared with BASDAI but this has only a marginal impact.
Keywords: ankylosing; economics; patient reported outcome measures; spondylitis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MvdS has received consulting fees/speaker’s fees/research grants from Novartis, UCB, Abbvie, Janssen, Eli Lilly and MSD. FAvG has received grants from Stichting vrienden van Sole Mio, Stichting ASAS, Jacobus Stichting, Novartis and UCB, and consulting fees from Novartis, Eli Lilly, MSD, AbbVie and Bristol Myers Squibb. MB has received consulting/speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen and Novartis. RR has received consulting/speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma. SE has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Janssen and Novartis. DvdH has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Cyxone, Daiichi, Eisai, Galapagos, Gilead, Glaxo-Smith-Kline, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, UCB Pharma and serves as director of Imaging Rheumatology bv. PMM has received consulting/speaker’s fees from AbbVie, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Orphazyme, Pfizer, Roche and UCB Pharma.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
