Prognostic Utility of Procalcitonin, Presepsin, and the VACO Index for Predicting 30-day Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 35177561
- PMCID: PMC8859553
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.406
Prognostic Utility of Procalcitonin, Presepsin, and the VACO Index for Predicting 30-day Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
Background: Biomarkers and clinical indices have been investigated for predicting mortality in patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19). We explored the prognostic utility of procalcitonin (PCT), presepsin, and the Veterans Health Administration COVID-19 (VACO) index for predicting 30-day-mortality in COVID-19 patients.
Methods: In total, 54 hospitalized COVID-19 patients were enrolled. PCT and presepsin levels were measured using the Elecsys BRAHMS PCT assay (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) and HISCL Presepsin assay (Sysmex, Kobe, Japan), respectively. The VACO index was calculated based on age, sex, and comorbidities. PCT and presepsin levels and the VACO index were compared using ROC curve, Kaplan-Meier method, and reclassification analysis for the 30-day mortality.
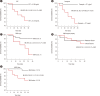
Results: ROC curve analysis was used to measure PCT and presepsin levels and the VACO index to predict 30-day mortality; the optimal cut-off values were 0.138 ng/mL for PCT, 717 pg/mL for presepsin, and 12.1% for the VACO index. On Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, hazard ratios (95% confidence interval) were 15.9 (4.1-61.3) for PCT, 26.3 (6.4-108.0) for presepsin, and 6.0 (1.7-21.1) for the VACO index. On reclassification analysis, PCT and presepsin in addition to the VACO index significantly improved the prognostic value of the index.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated the prognostic utility of measuring PCT and presepsin levels and the VACO index in COVID-19 patients. The biomarkers in addition to the clinical index were more useful than the index alone for predicting clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: 30-Day mortality; COVID-19; Prediction; Presepsin; Procalcitonin; VACO index.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Presepsin versus other biomarkers to predict sepsis and septic shock in patients with infection defined by Sepsis-3 criteria: the PREDI study of diagnostic accuracy.Emergencias. 2019 Oct;31(5):311-317. Emergencias. 2019. PMID: 31625302 English, Spanish.
-
The combination of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein or presepsin alone improves the accuracy of diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Crit Care. 2018 Nov 21;22(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2236-1. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30463590 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of presepsin and procalcitonin in non-infectious organ failure, sepsis, and septic shock: a prospective observational study according to the Sepsis-3 definitions.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Jan 4;22(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-07012-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34983420 Free PMC article.
-
Elevations in presepsin, PCT, hs-CRP, and IL-6 levels predict mortality among septic patients in the ICU.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Oct 1;116(4):890-900. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae121. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38776408
-
Presepsin as a diagnostic marker of sepsis in children and adolescents: a systemic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Aug 30;19(1):760. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4397-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31470804 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Performance of presepsin and procalcitonin predicting culture-proven bacterial infection and 28-day mortality: A cross sectional study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 22;9:954114. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.954114. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36072944 Free PMC article.
-
Novel approach exploring the correlation between presepsin and routine laboratory parameters using explainable artificial intelligence.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 1;10(13):e33826. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33826. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39027625 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Values of Procalcitonin and Presepsin for Acute Kidney Injury and 30-Day Hospital Mortality in Patients with COVID-19.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 May 28;58(6):727. doi: 10.3390/medicina58060727. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35743990 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Presepsin and Interferon-λ3 for Predicting Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 14;13(14):2372. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13142372. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510116 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Value and Diagnostic Potential of IL-10, IL-17A, IL1-β, IL-6, CXCL, and MCP for Severe COVID-19 and COVID-19 Mortality.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 10;12(7):1532. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071532. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, author. Current status of COVID-19 outbreak and vaccination in Korea (6.30.) [Updated on Nov 2021]. https://www.kdca.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20501010000&bid=0015&list_no=....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

