Performance Evaluation of the i-SmartCare 10 Analyzer and Method Comparison of Six Point-of-Care Blood Gas Analyzers
- PMID: 35177567
- PMCID: PMC8859550
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.467
Performance Evaluation of the i-SmartCare 10 Analyzer and Method Comparison of Six Point-of-Care Blood Gas Analyzers
Abstract
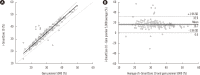
Blood gas, electrolyte, glucose, and lactate level measurement have an immediate and critical impact on patient care. We evaluated the performance of i-SmartCare 10 (i-SENS Inc., Seoul, Korea) and conducted a method comparison study of five point-of-care (POC) analyzers with i-SmartCare 10 as the comparator, according to the CLSI guidelines. Ten analytes (pH, pCO2, pO2, Na+, K+, Cl-, iCa2+, glucose, lactate, and Hct) were tested on six analyzers: i-SmartCare 10, ABL90 FLEX PLUS (Radiometer Medical ApS, Copenhagen, Denmark), i-Stat (Abbott Point of Care Inc., Princeton, NJ, USA), RapidLab 1265 (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc., Tarrytown, NY, USA), Stat Profile pHOx Ultra (Nova Biomedical, Waltham, MA, USA), and Gem Premier 5000 (Instrumentation Laboratory, Bedford, MA, USA). The total imprecision and linearity (r2>0.99) were excellent, except for a few analytes that narrowly escaped the preset criteria. Interference was noted for Na+ in the presence of a high K+ level and for iCa2+ in the presence of high K+ and Mg2+ levels. Forty of 48 items demonstrated either a proportional or systematic difference in regression analysis; the relative mean difference (%) of 14/48 items escaped the allowable total error in the difference plot analysis. i-SmartCare 10 shows acceptable performance, and using a single POC blood gas analyzer is recommended for monitoring.
Keywords: Analytical performance evaluation; Blood gas analyzer; Method comparison; Point-of-care; i-SmartCare 10.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

