Glia Regulate the Development, Function, and Plasticity of the Visual System From Retina to Cortex
- PMID: 35177968
- PMCID: PMC8843846
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2022.826664
Glia Regulate the Development, Function, and Plasticity of the Visual System From Retina to Cortex
Abstract
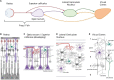
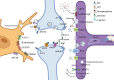
Visual experience is mediated through a relay of finely-tuned neural circuits extending from the retina, to retinorecipient nuclei in the midbrain and thalamus, to the cortex which work together to translate light information entering our eyes into a complex and dynamic spatio-temporal representation of the world. While the experience-dependent developmental refinement and mature function of neurons in each major stage of the vertebrate visual system have been extensively characterized, the contributions of the glial cells populating each region are comparatively understudied despite important findings demonstrating that they mediate crucial processes related to the development, function, and plasticity of the system. In this article we review the mechanisms for neuron-glia communication throughout the vertebrate visual system, as well as functional roles attributed to astrocytes and microglia in visual system development and processing. We will also discuss important aspects of glial function that remain unclear, integrating the knowns and unknowns about glia in the visual system to advance new hypotheses to guide future experimental work.
Keywords: Müller glia; astrocyte; microglia; neuron–glia interactions; ocular dominance plasticity; retina; visual cortex; visual system.
Copyright © 2022 Benfey, Foubert and Ruthazer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

