Safranal Prevents Liver Cancer Through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Alleviating Inflammation
- PMID: 35177980
- PMCID: PMC8845597
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.777500
Safranal Prevents Liver Cancer Through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Alleviating Inflammation
Abstract
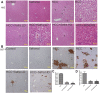
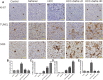
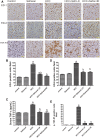
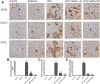
Despite all efforts, an effective and safe treatment for liver cancer remains elusive. Natural products and their derived biomolecules are potential resources to mine for novel anti-cancer drugs. Chemopreventive effects of safranal, a major bioactive ingredient of the golden spice "saffron", were evaluated in this study against diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced liver cancer in rats. Safranal's mechanisms of action were also investigated in the human liver cancer line "HepG2". When administered to DEN-treated rats, safranal significantly inhibited proliferation (Ki-67) and also induced apoptosis (TUNEL and M30 CytoDeath). It also exhibited anti-inflammatory properties where inflammatory markers such as NF-kB, COX2, iNOS, TNF-alpha, and its receptor were significantly inhibited. Safranal's in vivo effects were further supported in HepG2 cells where apoptosis was induced and inflammation was downregulated. In summary, safranal is reported here as a potent chemopreventive agent against hepatocellular carcinoma that may soon be an important ingredient of a broad-spectrum cancer therapy.
Keywords: inflammation; liver cancer; oxidative stress; prevention; safranal.
Copyright © 2022 Abdalla, Abdalla, Hamza and Amin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Saffron: a potential candidate for a novel anticancer drug against hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2011 Sep 2;54(3):857-67. doi: 10.1002/hep.24433. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21607999
-
Molecular Mechanisms behind Safranal's Toxicity to HepG2 Cells from Dual Omics.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 7;11(6):1125. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061125. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740022 Free PMC article.
-
Streptomyces Bioactive Metabolites Prevent Liver Cancer through Apoptosis, Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers in Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 29;11(4):1054. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041054. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189672 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Safranal and saffron stigma extracts in oxidative stress, diseases and photoaging: A systematic review.Heliyon. 2021 Feb 10;7(2):e06117. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06117. eCollection 2021 Feb. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33615006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological effects of Safranal: An updated review.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(10):1131-1143. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.69824.15197. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37736506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between COVID-19 and chronic liver disease: Mechanism, diagnosis, damage, and treatment.World J Virol. 2023 Jan 25;12(1):22-29. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v12.i1.22. World J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36743657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diosmin and Coenzyme q10: Synergistic histopathological and functional protection against doxorubicin-induced hepatorenal injury in rats.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Nov 30;13:101848. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101848. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39703765 Free PMC article.
-
Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling.Open Life Sci. 2025 Aug 1;20(1):20221009. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-1009. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40756571 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Crocin and Sorafenib Improves Their Tumor-Inhibiting Effects in a Rat Model of Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Cirrhotic-Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;15(16):4063. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164063. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627094 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Agrin in tissue repair and regeneration: From mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Nov;54(5):98. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5422. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39301653 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

