Molecular Assessment of Scutellaria barbata D. Don in the Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification
- PMID: 35178099
- PMCID: PMC8843875
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1988378
Molecular Assessment of Scutellaria barbata D. Don in the Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification
Abstract
Objective: To predict the molecular mechanisms behind the benefits of Scutellaria barbata D. Don (S. barbata) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) by network pharmacology and experimental verification.
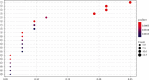
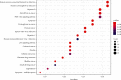
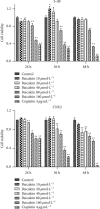
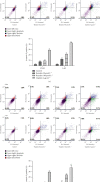
Methods: The active ingredients and targets of S. barbata were searched in the traditional Chinese medicine system pharmacology database and analysis platform, and the disease targets of NPC were obtained by searching the GeneCards database. A common target protein-protein interaction network was constructed by STRING, and then, an active ingredients-NPC-target interaction network map was constructed by Cytoscape 3.7.2 software. The functional enrichment analyses of Gene Ontology and KEGG pathway data were carried out by R software programming. Finally, cell proliferation was assessed by CCK8, apoptosis was detected by Annexin V-FITC/PI double fluorescence staining, and protein expression was analyzed by Western blotting.
Results: In this study, 29 active ingredients were found in S. barbata. Among these, the main targets for NPC were baicalein, wogonin, luteolin, and quercetin. The main molecular targets of S. barbata on NPC were EGFR, MYC, CASP3, CCND1, and ESR1. The main biological processes involved the binding of DNA-binding transcription factors, RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factors, ubiquitin-like protein ligases, and ubiquitin-protein ligases. S. barbata mainly affects NPC through the PI3K-Akt, p53, and MAPK signaling pathways. The experimental results showed that baicalein and wogonin could inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of NPC cells and downregulate the expression of PI3K, AKT, and p53, the key proteins of the PI3K/AKT and p53 signaling pathway in CNE2 cells.
Conclusion: Baicalein and wogonin, the main active ingredients of S. barbata, inhibited the proliferation and induced apoptosis of NPC cells through the PI3K/AKT and p53 signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2022 Hongjian Shi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

