Optimal Deep-Learning-Enabled Intelligent Decision Support System for SARS-CoV-2 Classification
- PMID: 35178226
- PMCID: PMC8846984
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4130674
Optimal Deep-Learning-Enabled Intelligent Decision Support System for SARS-CoV-2 Classification
Abstract
Intelligent decision support systems (IDSS) for complex healthcare applications aim to examine a large quantity of complex healthcare data to assist doctors, researchers, pathologists, and other healthcare professionals. A decision support system (DSS) is an intelligent system that provides improved assistance in various stages of health-related disease diagnosis. At the same time, the SARS-CoV-2 infection that causes COVID-19 disease has spread globally from the beginning of 2020. Several research works reported that the imaging pattern based on computed tomography (CT) can be utilized to detect SARS-CoV-2. Earlier identification and detection of the diseases is essential to offer adequate treatment and avoid the severity of the disease. With this motivation, this study develops an efficient deep-learning-based fusion model with swarm intelligence (EDLFM-SI) for SARS-CoV-2 identification. The proposed EDLFM-SI technique aims to detect and classify the SARS-CoV-2 infection or not. Also, the EDLFM-SI technique comprises various processes, namely, data augmentation, preprocessing, feature extraction, and classification. Moreover, a fusion of capsule network (CapsNet) and MobileNet based feature extractors are employed. Besides, a water strider algorithm (WSA) is applied to fine-tune the hyperparameters involved in the DL models. Finally, a cascaded neural network (CNN) classifier is applied for detecting the existence of SARS-CoV-2. In order to showcase the improved performance of the EDLFM-SI technique, a wide range of simulations take place on the COVID-19 CT data set and the SARS-CoV-2 CT scan data set. The simulation outcomes highlighted the supremacy of the EDLFM-SI technique over the recent approaches.
Copyright © 2022 Ashit Kumar Dutta et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




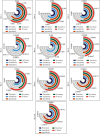
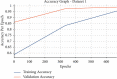
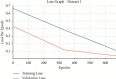
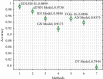

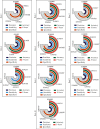
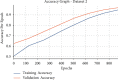
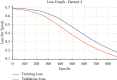
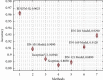
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

