Suspected Case of Drug-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome following Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Treatment
- PMID: 35178280
- PMCID: PMC8843409
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1714707
Suspected Case of Drug-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome following Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Treatment
Abstract
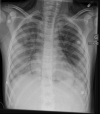
In this article, we reported the case of a child patient who was admitted to our PICU for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) while being treated with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) for osteomyelitis. Based on the timing of exposure, lack of alternative explanations, and clinical course similar to previously described cases, we suspect that TMP-SMX may have triggered ARDS. Despite meeting criteria for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation cannulation, conservative management and lung recruitment with high-frequency percussive ventilation could avoid the latter.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; percussive ventilation; trimethoprim.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Cheifetz I M. Pediatric ARDS. Respir Care. 2017;62(06):718–731. - PubMed
-
- Gutman L T. The use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in children: a review of adverse reactions and indications. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984;3(04):349–357. - PubMed
-
- Kongpan T, Mahasirimongkol S, Konyoung P et al. Candidate HLA genes for prediction of co-trimoxazole-induced severe cutaneous reactions. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2015;25(08):402–411. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

