Emerging Roles of COX7RP and Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35178385
- PMCID: PMC8844363
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.717881
Emerging Roles of COX7RP and Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Breast Cancer
Abstract
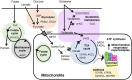
Metabolic alterations are critical events in cancers, which often contribute to tumor pathophysiology. While aerobic glycolysis is a known characteristic of cancer-related metabolism, recent studies have shed light on mitochondria-related metabolic pathways in cancer biology, including oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), amino acid and lipid metabolism, nucleic acid metabolism, and redox regulation. Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women; thus, elucidation of breast cancer-related metabolic alteration will help to develop cancer drugs for many patients. We here aim to define the contribution of mitochondrial metabolism to breast cancer biology. The relevance of OXPHOS in breast cancer has been recently defined by the discovery of COX7RP, which promotes mitochondrial respiratory supercomplex assembly and glutamine metabolism: the latter is also shown to promote nucleic acid and fatty acid biosynthesis as well as ROS defense regulation. In this context, the estrogen-related receptor (ERR) family nuclear receptors and collaborating coactivators peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1 (PGC-1) are essential transcriptional regulators for both energy production and cancer-related metabolism. Summarizing recent findings of mitochondrial metabolism in breast cancer, this review will aim to provide a clue for the development of alternative clinical management by modulating the activities of responsible molecules involved in disease-specific metabolic alterations.
Keywords: ERR; OxPhos; breast cancer; metabolism; mitochondria.
Copyright © 2022 Kamada, Takeiwa, Ikeda, Horie and Inoue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ariazi E. A., Clark G. M., Mertz J. E. (2002). Estrogen-Related Receptor Alpha and Estrogen-Related Receptor Gamma Associate with Unfavorable and Favorable Biomarkers, Respectively, in Human Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 62, 6510–6518. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

