Neonatal amygdala resting-state functional connectivity and socio-emotional development in very preterm children
- PMID: 35178519
- PMCID: PMC8846580
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac009
Neonatal amygdala resting-state functional connectivity and socio-emotional development in very preterm children
Abstract
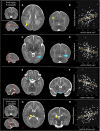
Very preterm children are more likely to exhibit difficulties in socio-emotional processing than their term-born peers. Emerging socio-emotional problems may be partly due to alterations in limbic system development associated with infants' early transition to extrauterine life. The amygdala is a key structure in this system and plays a critical role in various aspects of socio-emotional development, including emotion regulation. The current study tested the hypothesis that amygdala resting-state functional connectivity at term-equivalent age would be associated with socio-emotional outcomes in childhood. Participants were 129 very preterm infants (<33 weeks' gestation) who underwent resting-state functional MRI at term and received a neurodevelopmental assessment at 4-7 years (median = 4.64). Using the left and right amygdalae as seed regions, we investigated associations between whole-brain seed-based functional connectivity and three socio-emotional outcome factors which were derived using exploratory factor analysis (Emotion Moderation, Social Function and Empathy), controlling for sex, neonatal sickness, post-menstrual age at scan and social risk. Childhood Emotion Moderation scores were significantly associated with neonatal resting-state functional connectivity of the right amygdala with right parahippocampal gyrus and right middle occipital gyrus, as well as with functional connectivity of the left amygdala with the right thalamus. No significant associations were found between amygdalar resting-state functional connectivity and either Social Function or Empathy scores. The current findings show that amygdalar functional connectivity assessed at term is associated with later socio-emotional outcomes in very preterm children.
Keywords: child development; resting-state fMRI; socio-emotional outcomes; very preterm.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson S, Marlow N. Preterm birth and childhood psychiatric disorders. Pediatr Res. 2011;69(5 Pt 2):11R–18R. - PubMed
-
- Briggs-Gowan MJ, Owens PL, Schwab-Stone ME, Leventhal JM, Leaf PJ, Horwitz SM. Persistence of psychiatric disorders in pediatric settings. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2003;42(11):1360–1369. - PubMed
-
- Burnett AC, Anderson PJ, Cheong J, Doyle LW, Davey CG, Wood SJ. Prevalence of psychiatric diagnoses in preterm and full-term children, adolescents and young adults: A meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2011;41(12):2463–2474. - PubMed
-
- Morris AR, Bora S, Austin NC, Woodward LJ. Mental health, neurodevelopmental, and family psychosocial profiles of children born very preterm at risk of an early-onset anxiety disorder. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2021;63(8):954–962. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
