The RASopathies: from pathogenetics to therapeutics
- PMID: 35178568
- PMCID: PMC8862741
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.049107
The RASopathies: from pathogenetics to therapeutics
Abstract
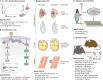
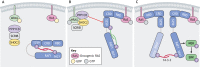
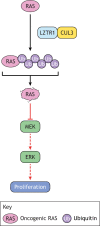
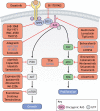
The RASopathies are a group of disorders caused by a germline mutation in one of the genes encoding a component of the RAS/MAPK pathway. These disorders, including neurofibromatosis type 1, Noonan syndrome, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, Costello syndrome and Legius syndrome, among others, have overlapping clinical features due to RAS/MAPK dysfunction. Although several of the RASopathies are very rare, collectively, these disorders are relatively common. In this Review, we discuss the pathogenesis of the RASopathy-associated genetic variants and the knowledge gained about RAS/MAPK signaling that resulted from studying RASopathies. We also describe the cell and animal models of the RASopathies and explore emerging RASopathy genes. Preclinical and clinical experiences with targeted agents as therapeutics for RASopathies are also discussed. Finally, we review how the recently developed drugs targeting RAS/MAPK-driven malignancies, such as inhibitors of RAS activation, direct RAS inhibitors and RAS/MAPK pathway inhibitors, might be leveraged for patients with RASopathies.
Keywords: Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome; Costello syndrome; Legius syndrome; Noonan syndrome; RAS; RASopathies.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abe, Y., Aoki, Y., Kuriyama, S., Kawame, H., Okamoto, N., Kurosawa, K., Ohashi, H., Mizuno, S., Ogata, T., Kure, S.et al. (2012). Prevalence and clinical features of Costello syndrome and cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome in Japan: findings from a nationwide epidemiological survey. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 158A, 1083-1094. 10.1002/ajmg.a.35292 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amyere, M., Revencu, N., Helaers, R., Pairet, E., Baselga, E., Cordisco, M., Chung, W., Dubois, J., Lacour, J.-P., Martorell, L.et al. (2017). Germline loss-of-function mutations in EPHB4 cause a second form of capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation (CM-AVM2) deregulating RAS-MAPK signaling. Circulation 136, 1037-1048. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.026886 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anastasaki, C., Estep, A. L., Marais, R., Rauen, K. A. and Patton, E. E. (2009). Kinase-activating and kinase-impaired cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome alleles have activity during zebrafish development and are sensitive to small molecule inhibitors. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, 2543-2554. 10.1093/hmg/ddp186 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andelfinger, G., Marquis, C., Raboisson, M.-J., Théoret, Y., Waldmüller, S., Wiegand, G., Gelb, B. D., Zenker, M., Delrue, M.-A. and Hofbeck, M. (2019). Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in Noonan syndrome treated by MEK-inhibition. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 73, 2237-2239. 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.066 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andreadi, C., Cheung, L.-K., Giblett, S., Patel, B., Jin, H., Mercer, K., Kamata, T., Lee, P., Williams, A., McMahon, M.et al. (2012). The intermediate-activity L597VBRAF mutant acts as an epistatic modifier of oncogenic RAS by enhancing signaling through the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Genes Dev. 26, 1945-1958. 10.1101/gad.193458.112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

