TDP-43 promotes tau accumulation and selective neurotoxicity in bigenic Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 35178571
- PMCID: PMC9066518
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.049323
TDP-43 promotes tau accumulation and selective neurotoxicity in bigenic Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
Although amyloid β (Aβ) and tau aggregates define the neuropathology of Alzheimer's disease (AD), TDP-43 has recently emerged as a co-morbid pathology in more than half of patients with AD. Individuals with concomitant Aβ, tau and TDP-43 pathology experience accelerated cognitive decline and worsened brain atrophy, but the molecular mechanisms of TDP-43 neurotoxicity in AD are unknown. Synergistic interactions among Aβ, tau and TDP-43 may be responsible for worsened disease outcomes. To study the biology underlying this process, we have developed new models of protein co-morbidity using the simple animal Caenorhabditis elegans. We demonstrate that TDP-43 specifically enhances tau but not Aβ neurotoxicity, resulting in neuronal dysfunction, pathological tau accumulation and selective neurodegeneration. Furthermore, we find that synergism between tau and TDP-43 is rescued by loss-of-function of the robust tau modifier sut-2. Our results implicate enhanced tau neurotoxicity as the primary driver underlying worsened clinical and neuropathological phenotypes in AD with TDP-43 pathology, and identify cell-type specific sensitivities to co-morbid tau and TDP-43. Determining the relationship between co-morbid TDP-43 and tau is crucial to understand, and ultimately treat, mixed pathology AD.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid β (Aβ); Proteotoxicity; TDP-43; Tau.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

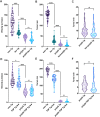
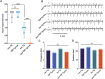

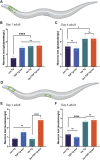


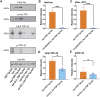
References
-
- Arai, T., Hasegawa, M., Akiyama, H., Ikeda, K., Nonaka, T., Mori, H., Mann, D., Tsuchiya, K., Yoshida, M., Hashizume, Y.et al. (2006). TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 602-611. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.093 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

