Visualizing cellular and tissue ultrastructure using Ten-fold Robust Expansion Microscopy (TREx)
- PMID: 35179128
- PMCID: PMC8887890
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.73775
Visualizing cellular and tissue ultrastructure using Ten-fold Robust Expansion Microscopy (TREx)
Erratum in
-
Correction: Visualizing cellular and tissue ultrastructure using Ten-fold Robust Expansion Microscopy (TREx).Elife. 2022 Nov 29;11:e85169. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85169. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36444779 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Expansion microscopy (ExM) is a powerful technique to overcome the diffraction limit of light microscopy that can be applied in both tissues and cells. In ExM, samples are embedded in a swellable polymer gel to physically expand the sample and isotropically increase resolution in x, y, and z. The maximum resolution increase is limited by the expansion factor of the gel, which is four-fold for the original ExM protocol. Variations on the original ExM method have been reported that allow for greater expansion factors but at the cost of ease of adoption or versatility. Here, we systematically explore the ExM recipe space and present a novel method termed Ten-fold Robust Expansion Microscopy (TREx) that, like the original ExM method, requires no specialized equipment or procedures. We demonstrate that TREx gels expand 10-fold, can be handled easily, and can be applied to both thick mouse brain tissue sections and cultured human cells enabling high-resolution subcellular imaging with a single expansion step. Furthermore, we show that TREx can provide ultrastructural context to subcellular protein localization by combining antibody-stained samples with off-the-shelf small-molecule stains for both total protein and membranes.
Keywords: cell biology; expansion microscopy; human; immunofluorescence; light microscopy; mouse; neuroscience; sub-organelle imaging; super-resolution.
© 2022, Damstra et al.
Conflict of interest statement
HD, BM, ME, AA, LK, PT No competing interests declared
Figures


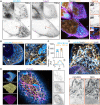
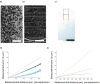
References
-
- Berg S, Kutra D, Kroeger T, Straehle CN, Kausler BX, Haubold C, Schiegg M, Ales J, Beier T, Rudy M, Eren K, Cervantes JI, Xu B, Beuttenmueller F, Wolny A, Zhang C, Koethe U, Hamprecht FA, Kreshuk A. ilastik: interactive machine learning for (bio)image analysis. Nature Methods. 2019;16:1226–1232. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0582-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bogovic JA, Hanslovsky P, Wong A, Saalfeld S. 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2016). Robust registration of calcium images by learned contrast synthesis; 2016. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

