Exosome-mediated genetic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages by exoASO-STAT6 leads to potent monotherapy antitumor activity
- PMID: 35179953
- PMCID: PMC8856615
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abj7002
Exosome-mediated genetic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages by exoASO-STAT6 leads to potent monotherapy antitumor activity
Abstract
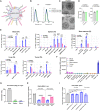
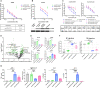
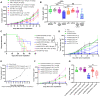
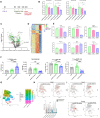
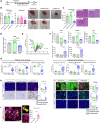
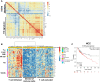
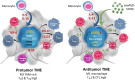
Effectiveness of checkpoint immunotherapy in cancer can be undermined by immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) with an M2 phenotype. Reprogramming TAMs toward a proinflammatory M1 phenotype is a novel approach to induce antitumor immunity. The M2 phenotype is controlled by key transcription factors such as signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6), which have been "undruggable" selectively in TAMs. We describe an engineered exosome therapeutic candidate delivering an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) targeting STAT6 (exoASO-STAT6), which selectively silences STAT6 expression in TAMs. In syngeneic models of colorectal cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma, exoASO-STAT6 monotherapy results in >90% tumor growth inhibition and 50 to 80% complete remissions. Administration of exoASO-STAT6 leads to induction of nitric oxide synthase 2 (NOS2), an M1 macrophage marker, resulting in remodeling of the tumor microenvironment and generation of a CD8 T cell-mediated adaptive immune response. Collectively, exoASO-STAT6 represents the first platform targeting transcription factors in TAMs in a highly selective manner.
Figures
References
-
- Schreiber R. D., Old L. J., Smyth M. J., Cancer immunoediting: Integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science 331, 1565–1570 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

