Flexible rerouting of hippocampal replay sequences around changing barriers in the absence of global place field remapping
- PMID: 35180390
- PMCID: PMC9473153
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.02.002
Flexible rerouting of hippocampal replay sequences around changing barriers in the absence of global place field remapping
Abstract
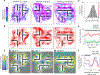
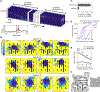
Flexibility is a hallmark of memories that depend on the hippocampus. For navigating animals, flexibility is necessitated by environmental changes such as blocked paths and extinguished food sources. To better understand the neural basis of this flexibility, we recorded hippocampal replays in a spatial memory task where barriers as well as goals were moved between sessions to see whether replays could adapt to new spatial and reward contingencies. Strikingly, replays consistently depicted new goal-directed trajectories around each new barrier configuration and largely avoided barrier violations. Barrier-respecting replays were learned rapidly and did not rely on place cell remapping. These data distinguish sharply between place field responses, which were largely stable and remained tied to sensory cues, and replays, which changed flexibly to reflect the learned contingencies in the environment and suggest sequenced activations such as replay to be an important link between the hippocampus and flexible memory.
Keywords: adaptation; attractor dynamics; barriers; hippocampus; memory; place cells; replay; sequences; spatial navigation.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
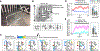
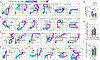

Comment in
-
Mental replays enable flexible navigation.Nature. 2022 May;605(7908):35-36. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-01035-0. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35422460 No abstract available.
-
Route selection with a cognitive map.Neuron. 2022 May 4;110(9):1441-1442. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.04.015. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 35512636
References
-
- Ainge JA, Tamosiunaite M, Wörgötter F, and Dudchenko PA (2012). Hippocampal place cells encode intended destination, and not a discriminative stimulus, in a conditional T-maze task. Hippocampus 22, 534–543. - PubMed
-
- Alvernhe A, Save E, and Poucet B (2011). Local remapping of place cell firing in the Tolman detour task. Eur. J. Neurosci. 33, 1696–1705. - PubMed
-
- Alvernhe A, Sargolini F, and Poucet B (2012). Rats build and update topological representations through exploration. Anim. Cogn. 15, 359–368. - PubMed

