COVID-19 pandemic and the effect of increased utilisation of mobile X-ray examinations on radiation dose to radiographers
- PMID: 35180810
- PMCID: PMC9088417
- DOI: 10.1002/jmrs.570
COVID-19 pandemic and the effect of increased utilisation of mobile X-ray examinations on radiation dose to radiographers
Abstract
Introduction: The use of ionising radiation results in occupational exposure to medical imaging professionals, requiring routine monitoring. This study aims to assess the effect of increased utilisation of mobile X-ray units, mobile imaging of non-routine body regions and radiographer work practice changes for impact on staff radiation dose during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of general radiology departments across two metropolitan hospitals was performed. Personal radiation monitor exposure reports between January 2019 and December 2020 were analysed. Statistical analysis was conducted using a Mann-Whitney U test when comparing each quarter, from 2019 to 2020. Categorical data were compared using a Chi-squared test.
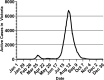
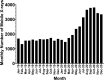
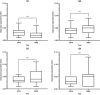
Results: Mobile X-ray use during the pandemic increased approximately 1.7-fold, with the peak usage observed in September 2020. The mobile imaging rate per month of non-routine body regions increased from approximately 6.0-7.8%. Reported doses marginally increased during Q2, Q3 and Q4 of 2020 (in comparison to 2019 data), though was not statistically significant (Q2: P = 0.13; Q3: P = 0.31 and Q4 P = 0.32). In Q1, doses marginally decreased and were not statistically significant (P = 0.22).
Conclusion: Increased utilisation and work practice changes had no significant effect on reported staff radiation dose. The average reported dose remained significantly lower than the occupational dose limits for radiation workers of 20 mSv.
Keywords: Clinical site; general; general radiography; medical imaging; radiation effects; respiratory.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Medical Radiation Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian Society of Medical Imaging and Radiation Therapy and New Zealand Institute of Medical Radiation Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Director‐General's opening remarks at the media briefing on. [press release], 2020.
-
- Health Do Coronavirus (COVID‐19) current situation and case numbers [Web Page]. Department of Health, Australian Government ; 2020. [updated 9 November 2020]. Available from: https://www.health.gov.au/news/health‐alerts/novel‐coronavirus‐2019‐ncov....
-
- Control ECfDPa . COVID‐19 situation update worldwide, as of week 7 2021. [updated 25th February 2021]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical‐distribution‐2019‐ncov‐cases
-
- First confirmed case of novel coronavirus in Australia [press release]. Department of Health Australia, 2021.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

