Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy
- PMID: 35180868
- PMCID: PMC8855550
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01509-9
Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy
Abstract
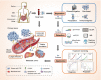
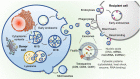
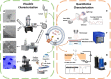
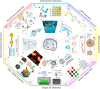
Liquid biopsy, characterized by minimally invasive detection through biofluids such as blood, saliva, and urine, has emerged as a revolutionary strategy for cancer diagnosis and prognosis prediction. Exosomes are a subset of extracellular vesicles (EVs) that shuttle molecular cargoes from donor cells to recipient cells and play a crucial role in mediating intercellular communication. Increasing studies suggest that exosomes have a great promise to serve as novel biomarkers in liquid biopsy, since large quantities of exosomes are enriched in body fluids and are involved in numerous physiological and pathological processes. However, the further clinical application of exosomes has been greatly restrained by the lack of high-quality separation and component analysis methods. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview on the conventional and novel technologies for exosome isolation, characterization and content detection. Additionally, the roles of exosomes serving as potential biomarkers in liquid biopsy for the diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and prognosis prediction of cancer are summarized. Finally, the prospects and challenges of applying exosome-based liquid biopsy to precision medicine are evaluated.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer; Exosome; Liquid biopsy; Precision medicine.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Caby M-P, Lankar D, Vincendeau-Scherrer C, Raposo G, Bonnerot C. Exosomal-like vesicles are present in human blood plasma. Int Immunol. 2005;17:879–887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

