Performances of rapid and connected salivary RT-LAMP diagnostic test for SARS-CoV-2 infection in ambulatory screening
- PMID: 35181680
- PMCID: PMC8857239
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-04826-7
Performances of rapid and connected salivary RT-LAMP diagnostic test for SARS-CoV-2 infection in ambulatory screening
Abstract
In the context of social events reopening and economic relaunch, sanitary surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 infection is still required. Here, we evaluated the diagnostic performances of a rapid, extraction-free and connected reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay on saliva. Nasopharyngeal (NP) swabs and saliva from 443 outpatients were collected simultaneously and tested by reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) as reference standard test. Seventy-one individuals (16.0%) were positive by NP and/or salivary RT-qPCR. Sensitivity and specificity of salivary RT-LAMP were 85.9% (95%CI 77.8-94.0%) and 99.5% (98.7-100%), respectively. Performances were similar for symptomatic and asymptomatic participants. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 genetic variants were analyzed and no dominant mutation in RT-LAMP primer region was observed during the period of the study. We demonstrated that this RT-LAMP test on self-collected saliva is reliable for SARS-CoV-2 detection. This simple connected test with optional automatic results transfer to health authorities is unique and opens the way to secure professional and social events in actual context of economics restart.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
F.S.S, J.E., J.B. and M.D. are employees of SkillCell. C.C., D.D. and P.K. are listed as inventors on a pending patent application on EasyCOV® Reader and hold shares of Vogo. A.P.L. is the CEO of SkillCell and holds shares of Alcen, mother company of SkillCell. F.M. is listed as inventor on a pending patent application on the diagnostic use of EasyCOV® and holds shares in SkillCell. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
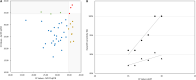
 show sensitivity (%) of RT-LAMP against salivary RT-qPCR (R2 = 0.92). Triangles
show sensitivity (%) of RT-LAMP against salivary RT-qPCR (R2 = 0.92). Triangles  show sensitivity (%) of salivary RT-LAMP compared to NP RT-qPCR (R2 = 0.61). RT-qPCR, reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction; RT-LAMP, reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification; NP, nasopharyngeal; Sal, salivary; Ct, cycle threshold. (B) Comparison of Ct Value between NP and salivary RT-qPCR. Dots represent experimentally measured Ct values of nasopharyngeal (X) and salivary (Y) RT-qPCR. Positive concordant individuals (positive for both NP and salivary RT-qPCR) are in down left white corner
show sensitivity (%) of salivary RT-LAMP compared to NP RT-qPCR (R2 = 0.61). RT-qPCR, reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction; RT-LAMP, reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification; NP, nasopharyngeal; Sal, salivary; Ct, cycle threshold. (B) Comparison of Ct Value between NP and salivary RT-qPCR. Dots represent experimentally measured Ct values of nasopharyngeal (X) and salivary (Y) RT-qPCR. Positive concordant individuals (positive for both NP and salivary RT-qPCR) are in down left white corner  . Negative concordant individuals (Ct value ≥ 35 for both NP and salivary RT-qPCR) are in upper right white corner
. Negative concordant individuals (Ct value ≥ 35 for both NP and salivary RT-qPCR) are in upper right white corner  . Discordant results (negative for one specimen and positive for the other in RT-qPCR) are on the grey zones of the graphic (NP+/Sal-
. Discordant results (negative for one specimen and positive for the other in RT-qPCR) are on the grey zones of the graphic (NP+/Sal-  ; NP-/Sal+
; NP-/Sal+ ).
).References
-
- Chan JF, Zhang AJ, Yuan S, et al. Simulation of the clinical and pathological manifestations of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a golden syrian hamster model: Implications for disease pathogenesis and transmissibility. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020;71(9):2428–2446. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa325. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

