Comparable results between crosslinked polyethylene and conventional ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene implanted in total knee arthroplasty: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials
- PMID: 35182171
- PMCID: PMC9418273
- DOI: 10.1007/s00167-022-06879-7
Comparable results between crosslinked polyethylene and conventional ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene implanted in total knee arthroplasty: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials
Abstract
Purpose: Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) has experienced exponential growth over the last decade, including increasingly younger patients with high functional demands. Highly crosslinked polyethylene (HXLPE) has been proven effective in reducing osteolysis and loosening revisions while improving long-term survival and performance in total hip arthroplasty; nevertheless, this superiority is not demonstrated in TKA. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to examine whether HXLPE improved overall survival and postoperative functional and radiological outcomes compared to conventional polyethylene (CPE) in TKA.
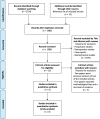
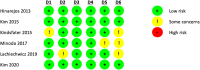
Methods: According to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guideline, a literature search of five databases (PubMed, Medline, Scopus, Science Direct and Embase) was made. A PICOS model was performed. The initial screening identified 2541 studies. Each eligible clinical article was analysed according to the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine 2011 Levels of Evidence (LoE). Only randomised clinical trials (RCTs) of LoE 1 and 2 were included. The methodological quality of the articles was assessed using the Risk of Bias 2 (RoB 2) tool.
Results: Six clinical studies were included in the final study. This systematic review and meta-analysis were registered on the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO). A total of 2285 knees were included. Eight outcomes (total reoperations, reoperations for prosthesis loosening and infections, radiolucent lines, osteolysis, mechanical failure, postoperative KSS knee score and function score) were analysed. For none of them, a statistically significant difference was found about the superiority of HXLPE over CPE (p > 0.05).
Conclusions: There were no statistically significant differences between HXLPE and CPE for TKA concerning clinical, radiological, and functional outcomes; nevertheless, HXLPE did not show higher failure rates or complications and can be safely used for TKA.
Level of evidence: II.
Keywords: CPE; Crosslinked; Knee; Meta-analysis; Polyethylene; Total knee arthroplasty; UHMWPE.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict to declare. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Figures
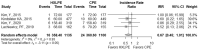
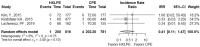

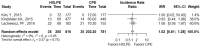
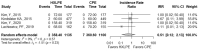

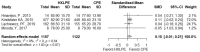
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

