Anti-CD20-atezolizumab-polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed/refractory follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 35182224
- PMCID: PMC9931830
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-021-03847-5
Anti-CD20-atezolizumab-polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed/refractory follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Purpose: New therapies are needed for relapsed/refractory (R/R) B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. This phase 1b, open-label trial evaluated two anti-CD20-based triplet combinations.
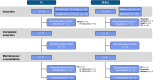
Methods: Patients with R/R follicular lymphoma (FL; n = 13) were treated with obinutuzumab, atezolizumab, and polatuzumab vedotin (G-atezo-pola; 1.4 mg/kg/1.8 mg/kg) and patients with R/R diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL; n = 23) received rituximab (R)-atezo-pola. The primary efficacy endpoint was complete response (CR) at end of induction (EOI) by PET-CT (investigator assessed; modified Lugano 2014 criteria). Safety endpoints were also assessed.
Results: 13 FL patients were treated and evaluable for safety; 2/23 DLBCL patients did not receive treatment and were not included in the safety population. Median observation time was 23.3 and 5.7 months in the FL and DLBCL cohorts, respectively. At EOI, CR rates in FL patients treated with G-atezo-pola at pola doses of 1.4 mg/kg (N = 3) and 1.8 mg/kg (N = 7) were 33% and 14%, respectively. In DLBCL patients receiving R-atezo-pola, the CR rate at EOI was 13%. In the FL cohort, 62% of patients experienced a grade 3-5 adverse event (AE; including two deaths) and 31% developed a serious AE (SAE). In DLBCL patients, R-atezo-pola was associated with a lower incidence of grade 3-5 AEs (24%; one death) and SAEs (10%). In both cohorts, the most common grade 3-5 AEs were hematologic toxicities.
Conclusion: Based on these safety issues, considered as related specifically to G-atezo-pola, and limited efficacy, no further development of either combination is planned.
Trial registration: NCT02729896; Date of registration: April 6, 2016.
Keywords: B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; Follicular lymphoma; Immunotherapy; Relapsed/refractory.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
H.E. reported: research funding, honoraria, or consulting fees from AbbVie, Genentech, Inc., Kite, Gilead Sciences, Takeda, Acerta, AstraZeneca, BeiGene and Juno. M.T. reported: research grants from Amgen, Gilead Sciences, Macrogenics, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, and Regeneron; consulting fees from Amgen and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd; and advisory board membership for Amgen and Regeneron. T.W. reported: research grants and advisory board membership for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Amgen, and Novartis; lecture fees from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Novartis, and Celgene; and advisory board membership for Celgene. I.S.L. reported: advisory board membership for Seattle Genetics and Janssen Scientific. J.W. reported: advisory board membership for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Celgene, Takeda, Janssen-Cilag, Servier, Amgen, BMS, Incyte, and AbbVie; research funding from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, GSK/Novartis, Takeda, Janssen-Cilag, and AbbVie; lecture honoraria from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Celgene, Takeda, Janssen-Cilag, and Servier; and conference travel support from Roche. U.B. reported: advisory board membership for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MSD, and Hexal; and travel grants from Janssen, Amgen, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, and Gilead Sciences. A.H. reported: research support by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Novartis, BMS, Pfizer, and Incyte. E.L.M. reported: advisory board membership for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Gilead Sciences, Takeda, Janssen-Cilag, Amgen, Novartis, AbbVie, and Celgene; lecture honoraria from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Janssen-Cilag, Amgen; and conference travel support from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Janssen-Cilag, and Amgen. W.K-P. declared no disclosures to report. A.S.K reports that West Virginia University, WV, USA directly received research funding outside the submitted work. T.N., S.C., M.S. and G.S. declared employment at F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd/Genentech, Inc. T.N. declared stock ownership at F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd/Genentech, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Thompson JA (2018) Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Summary. J Oncol Pract 14:247–249. 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6385 - PubMed
-
- Cheson BD, Ansell S, Schwartz L et al (2016a) Refinement of the Lugano Classification lymphoma response criteria in the era of immunomodulatory therapy. Blood 128:2489–2496. 10.1182/blood-2016-05-718528 - PubMed
-
- Collins LK, Chapman MS, Carter JB, Samie FH (2017) Cutaneous adverse effects of the immune checkpoint inhibitors. Curr Probl Cancer 41:125–128. 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2016.12.001 - PubMed
-
- Dai S, Jia R, Zhang X, Fang Q, Huang L (2014) The PD-1/PD-Ls pathway and autoimmune diseases. Cell Immunol 290:72–79. 10.1016/j.cellimm.2014.05.006 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

