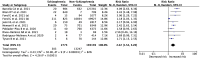Mortality from coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) in patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression
- PMID: 35182908
- PMCID: PMC8813760
- DOI: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2022.01.010
Mortality from coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) in patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression
Abstract
Objective: Schizophrenia has been associated with patients' poor quality of life, disability, and hospitalization. As of today, evidence that highlights the association between schizophrenia and coronavirus disease (Covid-19) outcomes remains unclear. This study sought to analyze whether patients with pre-existing schizophrenia are at higher risk for Covid-19 mortality.
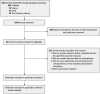
Methods: Using specific keywords, we comprehensively searched PubMed, Scopus, OVID, and Cochrane Library sources until November 15th, 2021. All published studies on schizophrenia and Covid-19 were collected. We used Review Manager 5.4 and Comprehensive Meta-Analysis 3 software to conduct statistical analysis.
Results: There were 10 studies with 263,207 Covid-19 patients included in the analysis. Evaluation of the data gathered yielded an association between schizophrenia and increased mortality from Covid-19 (RR 2.22; 95%CI: 1.54-3.20, p < 0.00001, I2 = 82% random-effect model). The increased risk of developing mortality from Covid-19 in patients with schizophrenia was significantly influenced by older age (p = 0.0004) and smoking (p = 0.0048).
Conclusions: This study proposes that patients with pre-existing schizophrenia are at risk of developing higher Covid-19 mortality. Patients with schizophrenia need special attention and should be prioritized to receive the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Registration details: CRD42021293997.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Covid-19; Psychiatry; Psychosis; Schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): situation report. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on... Accessed November 22, 2021.
-
- Hariyanto T.I., Putri C., Hananto J.E., Arisa J., Situmeang Fransisca V., R, Kurniawan A. Delirium is a good predictor for poor outcomes from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. J Psychiatr Res. 2021 Oct;142(361–368) doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.08.031. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous