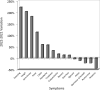
Analysis of online search trends suggests that SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant causes different symptoms
- PMID: 35183609
- PMCID: PMC8851877
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.02.011
Analysis of online search trends suggests that SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant causes different symptoms
Keywords: COVID-19; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; Symptoms; Variants.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no relevant competing interest to disclose in relation to this work.
Figures
Comment in
-
Infection with the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 is associated with less severe disease in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.J Infect. 2022 Nov;85(5):e152-e154. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.07.029. Epub 2022 Aug 6. J Infect. 2022. PMID: 35940349 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evolution of symptoms compatible with post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC) after Wild-type and/or Omicron BA.1 infection: A prospective healthcare worker cohort.J Infect. 2024 Feb;88(2):200-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2023.12.002. Epub 2023 Dec 7. J Infect. 2024. PMID: 38070691 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lippi G., Mattiuzzi C., Henry B.M. Updated picture of SARS-CoV-2 variants and mutations. Diagnosis. 2022;9:11–17. (Berl) - PubMed
-
- Mahase E. COVID-19: hospital admission 50–70% less likely with Omicron than delta, but transmission a major concern. BMJ. 2021;375:n3151. - PubMed
-
- Iacobucci G. COVID-19: runny nose, headache, and fatigue are commonest symptoms of Omicron, early data show. BMJ. 2021;375:n3103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous