Novel inhibitors of phosphorylation independent activity of GRK2 modulate cAMP signaling
- PMID: 35184416
- PMCID: PMC8858223
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.913
Novel inhibitors of phosphorylation independent activity of GRK2 modulate cAMP signaling
Abstract
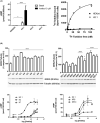
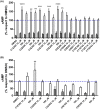
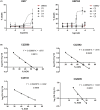
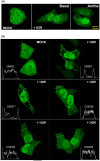
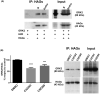
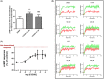
G protein-coupled receptors kinase 2 (GRK2) plays a major role in receptor regulation and, as a consequence, in cell biology and physiology. GRK2-mediated receptor desensitization is performed by its kinase domain, which exerts receptor phosphorylation promoting G protein uncoupling and the cessation of signaling, and by its RGS homology (RH) domain, able to interrupt G protein signaling. Since GRK2 activity is exacerbated in several pathologies, many efforts to develop inhibitors have been conducted. Most of them were directed toward GRK2 kinase activity and showed encouraging results on in vitro systems and animal models. Nevertheless, limitations including unspecific effects or pharmacokinetics issues prevented them from advancing to clinical trials. Surprisingly, even though the RH domain demonstrated the ability to desensitize GPCRs, this domain has been less explored. Herein, we show in vitro activity of a series of compounds that, by inhibiting GRK2 RH domain, increase receptor cAMP response, avoid GRK2 translocation to the plasma membrane, inhibit coimmunoprecipitation of GRK2 with Gαs subunit of heterotrimeric G protein, and prevent receptor desensitization. Also, we preliminarily evaluated candidates' ADMET properties and observed suitable lipophilicity and cytotoxicity. These novel inhibitors of phosphorylation-independent actions of GRK2 might be useful in elucidating other RH domain roles and lay the foundation for the development of innovative pharmacologic therapy for diseases where GRK2 activity is exacerbated.
Keywords: CADD; GPCR; GRK2; RGS; desensitization.
© 2022 The Authors. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd, British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of inhibitors of the RGS homology domain of GRK2 by docking-based virtual screening.Life Sci. 2019 Dec 15;239:116872. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116872. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31525427
-
Roles of phosphorylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms in the regulation of histamine H2 receptor by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 19;286(33):28697-28706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.269613. Epub 2011 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21705320 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Constitutive GPR3 Signaling and Surface Localization by GRK2 and β-arrestin-2 Overexpression in HEK293 Cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 27;8(6):e65365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065365. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826079 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory effects of GRK2 on GPCRs and non-GPCRs and possible use as a drug target (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2016 Oct;38(4):987-94. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2720. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27573285 Review.
-
Design of substrates and inhibitors of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) based on its phosphorylation reaction.Amino Acids. 2020 Jul;52(6-7):863-870. doi: 10.1007/s00726-020-02864-x. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Amino Acids. 2020. PMID: 32577910 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

