Social and Biological Parameters Involved in Suicide Ideation During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 35185341
- PMCID: PMC8851148
- DOI: 10.1177/1178646920978243
Social and Biological Parameters Involved in Suicide Ideation During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Narrative Review
Abstract
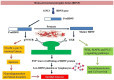
Fear is an indispensable characteristic of any infectious disease, and the alarm will be further amplified when the infection spreads uncontrollable, unpredictable, and global. The novel corona virus (SARS CoV-2) lead Covid-19, has been declared as a global emergency by WHO as it has affected millions of people with a high mortality rate. The non-availability of medicine for Covid-19 and the various control measures such as social distancing, self-isolation, house quarantine, and the new normal implementation by different nations across the world to control the spread of Covid-19 made people vulnerable to fear and anxiety. As a result, considerable number of Covid-19-related suicidal deaths has been reported across the world during this pandemic. There have been several studies which describe the psychosocial aspects of suicidal ideation. However, the research on the biological aspects of suicidal ideation/suicidal risk factors that are related to pandemic are unreported. Hence this review article is intended to provide a comprehensive analysis of suicidal deaths during Covid-19 and also aimed to addresses the possible link between suicidal ideation and different factors, including psycho-social, behavioral, neurobiological factors (proximal, distal, and inflammatory) and immunity. The alterations in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmitters had upregulated the GABARB3, GABARA4, GABARA3, GABARR1, GABARG2, and GAD2 gene expressions in suicidal victims. The changes in the Kynurenine (KYN) pathway, Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal axis (HPA axis) hyperactivation, and dysregulation of serotonin biosynthesis would significantly alter the brain chemistry in people with suicide ideation.
Keywords: Covid-19; inflammatory cytokines; neurobiological factors; psychiatric disorder; suicidal behavior; suicidal death.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Greek population: Suicidal ideation during the first and second lockdown.Psychiatriki. 2021 Dec 20;32(4):267-270. doi: 10.22365/jpsych.2021.041. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Psychiatriki. 2021. PMID: 34860683 English, Greek, Modern.
-
A prospective examination of COVID-19-related social distancing practices on suicidal ideation.Suicide Life Threat Behav. 2021 Oct;51(5):969-977. doi: 10.1111/sltb.12782. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Suicide Life Threat Behav. 2021. PMID: 34184290 Free PMC article.
-
[Suicidal behavior in light of COVID-19 outbreak: Clinical challenges and treatment perspectives].Encephale. 2020 Jun;46(3S):S66-S72. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2020.05.001. Epub 2020 May 8. Encephale. 2020. PMID: 32471707 Free PMC article. Review. French.
-
Suicidal ideation among Canadian adults during the COVID-19 pandemic: the role of psychosocial factors and substance use behaviours.BMC Psychiatry. 2022 Nov 16;22(1):711. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-04353-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36384538 Free PMC article.
-
Suicidal Behavior in the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022 Jan;24(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s11920-022-01312-9. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022. PMID: 35080711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suicidality and COVID-19: Suicidal ideation, suicidal behaviors and completed suicides amidst the COVID-19 pandemic (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jan;23(1):107. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.11030. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 34976149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential impact of Covid-19 on CNS and psychiatric sequels.Asian J Psychiatr. 2022 Jun;72:103097. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2022.103097. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Asian J Psychiatr. 2022. PMID: 35405524 Free PMC article.
-
Transcultural Comparison of Mental Health and Work-Life Integration Blurring in the Brazilian and Spanish Populations during COVID-19.J Pers Med. 2023 Jun 5;13(6):955. doi: 10.3390/jpm13060955. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37373944 Free PMC article.
-
'Why are you not dead yet?' - dimensions and the main driving forces of stigma and discrimination among COVID-19 patients in Sri Lanka.Public Health. 2021 Oct;199:10-16. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2021.07.001. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34517288 Free PMC article.
-
Suicide, neuroinflammation and other physiological alterations.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Aug;274(5):1037-1049. doi: 10.1007/s00406-023-01584-z. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 36913003 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

