Cardiovascular Pulsatility Increases in Visual Cortex Before Blood Oxygen Level Dependent Response During Stimulus
- PMID: 35185462
- PMCID: PMC8853630
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.836378
Cardiovascular Pulsatility Increases in Visual Cortex Before Blood Oxygen Level Dependent Response During Stimulus
Abstract
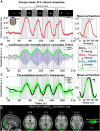
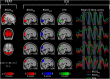
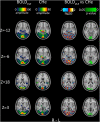
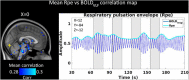
The physiological pulsations that drive tissue fluid homeostasis are not well characterized during brain activation. Therefore, we used fast magnetic resonance encephalography (MREG) fMRI to measure full band (0-5 Hz) blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLDFB) signals during a dynamic visual task in 23 subjects. This revealed brain activity in the very low frequency (BOLDVLF) as well as in cardiac and respiratory bands. The cardiovascular hemodynamic envelope (CHe) signal correlated significantly with the visual BOLDVLF response, considered as an independent signal source in the V1-V2 visual cortices. The CHe preceded the canonical BOLDVLF response by an average of 1.3 (± 2.2) s. Physiologically, the observed CHe signal could mark increased regional cardiovascular pulsatility following vasodilation.
Keywords: cardiovascular pulsations; fast fMRI; magnetic resonance encephalography; task activation; visual stimulation.
Copyright © 2022 Huotari, Tuunanen, Raitamaa, Raatikainen, Kananen, Helakari, Tuovinen, Järvelä, Kiviniemi and Korhonen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

