Single Point Insulin Sensitivity Estimator in Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 35185803
- PMCID: PMC8848352
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.830012
Single Point Insulin Sensitivity Estimator in Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
Background: Attenuated insulin-sensitivity (IS) is a central feature of pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). We recently developed a new index, single point insulin sensitivity estimator (SPISE), based on triglycerides, high-density-lipoprotein and body-mass-index (BMI), and validated by euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp-test (EHCT) in adolescents. This study aims to assess the performance of SPISE as an estimation of hepatic insulin (in-)sensitivity. Our results introduce SPISE as a novel and inexpensive index of hepatic insulin resistance, superior to established indices in children and adolescents with obesity.
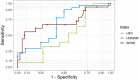
Materials and methods: Ninety-nine pubertal subjects with obesity (13.5 ± 2.0 years, 59.6% males, overall mean BMI-SDS + 2.8 ± 0.6) were stratified by MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) into a NAFLD (>5% liver-fat-content; male n=41, female n=16) and non-NAFLD (≤5%; male n=18, female n=24) group. Obesity was defined according to WHO criteria (> 2 BMI-SDS). EHCT were used to determine IS in a subgroup (n=17). Receiver-operating-characteristic (ROC)-curve was performed for diagnostic ability of SPISE, HOMA-IR (homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance), and HIRI (hepatic insulin resistance index), assuming null hypothesis of no difference in area-under-the-curve (AUC) at 0.5.
Results: SPISE was lower in NAFLD (male: 4.8 ± 1.2, female: 4.5 ± 1.1) than in non-NAFLD group (male 6.0 ± 1.6, female 5.6 ± 1.5; P< 0.05 {95% confidence interval [CI]: male NAFLD 4.5, 5.2; male non-NAFLD 5.2, 6.8; female NAFLD 4.0, 5.1, female non-NAFLD 5.0, 6.2}). In males, ROC-AUC was 0.71 for SPISE (P=0.006, 95% CI: 0.54, 0.87), 0.68 for HOMA-IR (P=0.038, 95% CI: 0.48, 0.88), and 0.50 for HIRI (P=0.543, 95% CI: 0.27, 0.74). In females, ROC-AUC was 0.74 for SPISE (P=0.006), 0.59 for HOMA-IR (P=0.214), and 0.68 for HIRI (P=0.072). The optimal cutoff-level for SPISE between NAFLD and non-NAFLD patients was 5.18 overall (Youden-index: 0.35; sensitivity 0.68%, specificity 0.67%).
Conclusion: SPISE is significantly lower in juvenile patients with obesity-associated NAFLD. Our results suggest that SPISE indicates hepatic IR in pediatric NAFLD patients with sensitivity and specificity superior to established indices of hepatic IR.
Keywords: HOMA-IR; hepatic insulin resistance index; insulin resistance; pediatric obesity; receiver-operating-characteristic curve.
Copyright © 2022 Furthner, Anderwald, Bergsten, Forslund, Kullberg, Ahlström, Manell, Ciba, Mangge, Maruszczak, Koren, Schütz, Brunner, Schneider, Weghuber and Mörwald.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

