Recent Advances in Understanding the Structure and Function of the Human Microbiome
- PMID: 35185849
- PMCID: PMC8851206
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.825338
Recent Advances in Understanding the Structure and Function of the Human Microbiome
Abstract
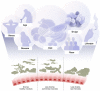
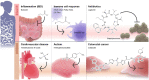
Trillions of microbes live within our bodies in a deep symbiotic relationship. Microbial populations vary across body sites, driven by differences in the environment, immunological factors, and interactions between microbial species. Major advances in genome sequencing enable a better understanding of microbiome composition. However, most of the microbial taxa and species of the human microbiome are still unknown. Without revealing the identity of these microbes as a first step, we cannot appreciate their role in human health and diseases. A shift in the microbial balance, termed dysbiosis, is linked to a broad range of diseases from simple colitis and indigestion to cancer and dementia. The last decade has witnessed an explosion in microbiome research that led to a better understanding of the microbiome structure and function. This understanding leads to potential opportunities to develop next-generation microbiome-based drugs and diagnostic biomarkers. However, our understanding is limited given the highly personalized nature of the microbiome and its complex and multidirectional interactions with the host. In this review, we discuss: (1) our current knowledge of microbiome structure and factors that shape the microbial composition, (2) recent associations between microbiome dysbiosis and diseases, and (3) opportunities of new microbiome-based therapeutics. We analyze common themes, promises, gaps, and challenges of the microbiome research.
Keywords: disease associations; fecal transplant; human microbiome; microbial diversity; probiotics.
Copyright © 2022 Mousa, Chehadeh and Husband.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abee T., Klaenhammer T. R., Letellier L. (1994). Kinetic studies of the action of lactacin F, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus johnsonii that forms poration complexes in the cytoplasmic membrane. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60, 1006–1013. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.3.1006-1013.1994, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ait-Belgnaoui A., Durand H., Cartier C., Chaumaz G., Eutamene H., Ferrier L., et al. (2012). Prevention of gut leakiness by a probiotic treatment leads to attenuated HPA response to an acute psychological stress in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37, 1885–1895. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.03.024, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

