Potentials of Non-Invasive 18F-FDG PET/CT in Immunotherapy Prediction for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 35186013
- PMCID: PMC8855498
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.810011
Potentials of Non-Invasive 18F-FDG PET/CT in Immunotherapy Prediction for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
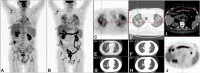
The immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), by targeting cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4, programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), or PD-ligand 1, have dramatically changed the natural history of several cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). There are unusual response manifestations (such as pseudo-progression, hyper-progression, and immune-related adverse events) observed in patients with ICIs because of the unique mechanisms of these agents. These specific situations challenge response and prognostic assessment to ICIs challenging. This review demonstrates how 18F-FDG PET/CT can help identify these unusual response patterns in a non-invasive and effective way. Then, a series of semi-quantitative parameters derived from 18F-FDG PET/CT are introduced. These indexes have been recognized as the non-invasive biomarkers to predicting the efficacy of ICIs and survival of NSCLC patients according to the latest clinical studies. Moreover, the current situation regarding the functional criteria based on 18F-FDG PET/CT for immunotherapeutic response assessment is presented and analyzed. Although the criteria based on 18F-FDG PET/CT proposed some resolutions to overcome limitations of morphologic criteria in the assessment of tumor response to ICIs, further researches should be performed to validate and improve these assessing systems. Then, the last part in this review displays the present status and a perspective of novel specific PET probes targeting key molecules relevant to immunotherapy in prediction and response assessment.
Keywords: FDG; NSCLC; PET/CT; immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI); immunotherapy; lung cancer; prognosis; response.
Copyright © 2022 Liao, Liu, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anwar H., Sachpekidis C., Winkler J., Kopp-Schneider A., Haberkorn U., Hassel J. C., et al. (2018). Absolute Number of New Lesions on 18F-FDG PET/CT Is More Predictive of Clinical Response Than SUV Changes in Metastatic Melanoma Patients Receiving Ipilimumab. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 45, 376–383. 10.1007/s00259-017-3870-6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barrón F., Cardona A. F., Cardona A. F., Corrales L., Ramirez-Tirado L.-A., Caballe-Perez E., et al. (2018). Characteristics of Progression to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Predict Overall Survival in Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring an EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Dis. 10, 2166–2178. 10.21037/jtd.2018.03.106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bensch F., van der Veen E. L., Lub-de Hooge M. N., Jorritsma-Smit A., Boellaard R., Kok I. C., et al. et al (2018). 89Zr-atezolizumab Imaging as a Non-invasive Approach to Assess Clinical Response to PD-L1 Blockade in cancerZr-Atezolizumab Imaging as a Non-invasive Approach to Assess Clinical Response to PD-L1 Blockade in Cancer. Nat. Med. 24, 1852–1858. 10.1038/s41591-018-0255-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

