The Protective Mechanism of Dexmedetomidine on Renal in Hemorrhagic Shock
- PMID: 35186114
- PMCID: PMC8856797
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6394544
The Protective Mechanism of Dexmedetomidine on Renal in Hemorrhagic Shock
Retraction in
-
Retracted: The Protective Mechanism of Dexmedetomidine on Renal in Hemorrhagic Shock.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9797024. doi: 10.1155/2023/9797024. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37416201 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To explore the protective effect of dexmedetomidine on renal function in patients with hemorrhagic shock and its possible mechanism.
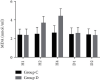
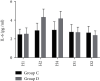
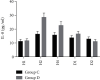
Methods: Seventy patients with traumatic hemorrhagic shock requiring surgical treatment were randomly divided into the control group (group C) and the dexmedetomidine group (group D), with 35 patients in each group. Patients in both groups were actively treated with volumetric resuscitation while surgical hemostasis. Group D was given dexmedetomidine 0.5 μg/kg before skin incision after anesthesia induction, for 10 min, followed by intravenous infusion at a rate of 0.4 μg·kg-1·h-1 until 30 min before surgery, and group C was given equal volume of normal saline before skin resection (H1). Venous blood was collected 2 h (H2) and 4 h (H4) after skin resection, and plasma levels of BUN, creatinine (SCr), lipid peroxides (MDA), and inflammatory mediators IL-6 and IL-8 were measured on the 1st and 2nd day after surgery.
Results: Compared with H1, BUN and SCr levels had no significant difference at 2 h and 4 h after skin resection but significantly decreased at 1 and 2 postoperative days (D1) (P < 0.05). There were significant differences in MDA, IL-6, and IL-8 at 2 and 4 h after skin resection (P < 0.05), but there were no significant differences at 1 day after surgery (D1) and 2 days after surgery (D2). Compared with group C, the levels of MDA, IL-6, and IL-8 in group U were significantly decreased at 2 h and 4 h after skin resection (P < 0.05), and the levels of BUN and SCr in group U were significantly decreased at 1 and 2 days after skin resection (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine can effectively inhibit the release of oxygen free radicals in the shock stage and the shock recovery stage in patients with hemorrhagic trauma shock and has a protective effect on renal function.
Copyright © 2022 Zhaojin Jia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravenous Vitamin C attenuates hemorrhagic shock-related renal injury through the induction of SIRT1 in rats.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jun 22;501(2):358-364. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.111. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29673592
-
Dexmedetomidine did not reduce the effects of tourniquet-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury during general anesthesia.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2013 Feb;29(2):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2012.08.013. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23347808 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Dexmedetomidine preconditioning protects against lung injury in hemorrhagic shock rats].Braz J Anesthesiol. 2019 Mar-Apr;69(2):160-167. doi: 10.1016/j.bjan.2018.09.011. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 30655009 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of intraoperative infusion of dexmedetomidine on early renal function after percutaneous nephrolithotomy.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011 May;55(5):539-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2011.02427.x. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011. PMID: 21827441
-
Dexmedetomidine controls systemic cytokine levels through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.Inflammation. 2014 Oct;37(5):1763-70. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9906-1. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24803295
Cited by
-
Retracted: The Protective Mechanism of Dexmedetomidine on Renal in Hemorrhagic Shock.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9797024. doi: 10.1155/2023/9797024. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37416201 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity and immunotherapy for hemorrhagic shock.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 25;13:918380. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.918380. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36091025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou Y., Dong X., Zhang L. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg . 2022. Dexmedetomidine Can Reduce the Level of Oxidative Stress and Serum miR-10a in Patients with Lung Cancer after Surgery. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources