Hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus: overview of current knowledge
- PMID: 35186126
- PMCID: PMC8848057
- DOI: 10.1177/1759720X211073001
Hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus: overview of current knowledge
Abstract
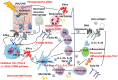
The antimalarial hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) has demonstrated several crucial properties for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Herein, we reviewed the main HCQ pharmacologic features, detailed its mechanism of action, and summarized the existing guidelines and recommendations for HCQ use in rheumatology with a systematic literature search for the randomized controlled trials focused on lupus. HCQ has been shown to decrease SLE activity, especially in mild and moderate disease, to prevent disease flare and to lower the long-term glucocorticoid need. The numerous benefits of HCQ are extended to pregnancy and breastfeeding period. Based on cohort studies, antithrombotic and metabolic HCQ's effects were shown, including lipid-lowering properties, which might contribute to an improved cardiovascular risk. Moreover, early HCQ use in antinuclear antibodies positive individuals might delay the progression to SLE. Finally, HCQ has a significant favorable impact on long-term outcomes such as damage accrual and mortality in SLE. Based on these multiple benefits, HCQ is now the mainstay long-term treatment in SLE, recommended by current guidelines in all patients unless contraindications or side effects. The daily dose associated with the best compromise between efficacy and safety is matter of debate. The concern regarding retinal toxicity rather than proper efficacy data is the one that dictated the daily dosage of ⩽5 mg/kg/day actual body weight currently agreed upon.
Keywords: antimalarials; cutaneous lupus erythematosus; hydroxychloroquine; immunomodulatory; lupus nephritis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Olsen NJ, Schleich MA, Karp DR. Multifaceted effects of hydroxychloroquine in human disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2013; 43: 264–272. - PubMed
-
- Dima A, Jurcut C, Arnaud L. Hydroxychloroquine in systemic and auto-immune diseases: where are we now? Jt Bone Spine 2021; 88: 105143. - PubMed
-
- Akhavan PS, Su J, Lou W, et al.. The early protective effect of hydroxychloroquine on the risk of cumulative damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 2013; 40: 831–841. - PubMed
-
- Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Leroux G, Piette JC, et al.. Why all systemic lupus erythematosus patients should be given hydroxychloroquine treatment. Joint Bone Spine 2010; 77: 4–5. - PubMed
-
- Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Dunogué B, Morel N, et al.. Hydroxychloroquine: a multifaceted treatment in lupus. Press Médicale 2014; 43: e167–e180. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources